Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150112-11
- Publication
- Geling et al., 2004 - Her5 acts as a prepattern factor that blocks neurogenin1 and coe2 expression upstream of Notch to inhibit neurogenesis at the midbrain-hindbrain boundary
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
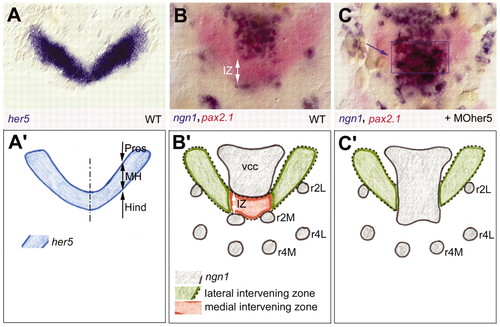
Her5 activity at the midbrain-hindbrain boundary and nomenclature. All top views (A-C) are flat-mounted embryos at the three-somite stage, dorsal views with anterior upwards, revealed by in situ hybridisation for expression of the genes indicated (colour-coded, left corner) (see also Geling et al., 2003). Bottom panels (A2-C2) are interpretative drawings of the embryos in A-C to introduce the specific nomenclature used in this work. At the three-somite stage, her5 expression (A) encompasses most of the presumptive MH (Tallafuss and Bally-Cuif, 2003) and separates the first ngn1-positive clusters (B) within the anterior neural plate. These are the ventrocaudal cluster (vcc), located in the basal diencephalon and anterior midbrain, the presumptive motoneurons (r2M) and lateral neuronal precursors (r2L) in rhombomere 2. The non-neurogenic domain identified by her5 positivity and ngn1 negativity around the MHB is called intervening zone (IZ) (white arrow in B,B2). (C) Upon blocking Her5 activity by injection of a her5 morpholino (MOher5) into wild-type embryos, the medial (future basal) part of the IZ domain is bridged by ectopic ngn1-positive cells (blue arrow and blue box in C, compare with B). Thus, the IZ is composed of a medial domain (red in B2, absent in C2, blue box in C) that crucially requires Her5, and of a lateral domain (green in B2 and C2) that exhibits additional blocks towards neurogenesis. Interpreted from (Geling et al., 2003). Hind, presumptive hindbrain; MH, mid-hindbrain domain; Pros, presumptive prosencephalon; r4M, motorneurons of rhombomere 4; r4L, lateral neuronal precursors in r4. |