|
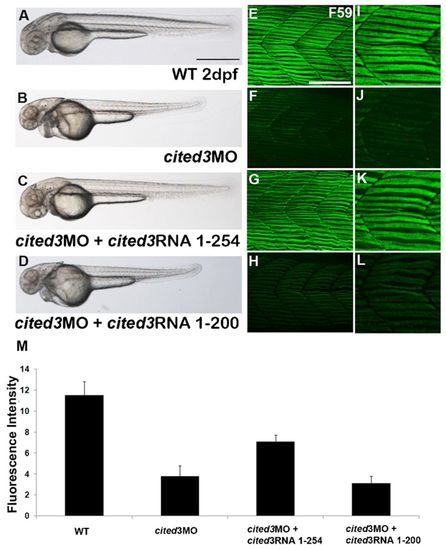
Knock down of cited3 disrupts muscle differentiation. (A,B) Knock down of cited3 with two splice-blocking morpholino oligonucleotides (MO), S1-MO and S2-MO, resulted in thinner and shorter trunk, and dilated heart (B) compared to wild-type embryos (A) or embryos injected with the control MO (data not shown). Coinjection of full length cited3 RNA (codes for 254 amino acid) rescued cited3 morphant phenotype (C). (D) In contrast, coinjection of a C-terminally truncated form of cited3 RNA (coding for the first 200 amino acids) did not rescue the morphant phenotype. (E) The expression of myosin heavy chain as evidenced by F59 antibody in an area covering somite 16th–18th in a wild-type embryo at 2 dpf. (F) The staining of F59 is reduced in embryos injected with cited3 MO, whereas the expression of myosin heavy chain was restored when cited3 RNA was co-injected with cited3 MO (G) but not rescued when cited31–200 RNA was coinjected (H). (I–L) Magnified images of F59 staining. (M) The graphical representation of the average fluorescent intensity measurement of F59 immunostaining (of 10–18 embryos from three different experiments). Intensity of F59 staining was significantly reduced in cited3 morphants when compared to that in wild-type (P-value<2×104), rescued when cited3 RNA was co-injected (P-value<2×102) but not rescued when cited31–200 RNA was coinjected (P-value>0.7). Scale bars: 100 μm in A and 50 μm in E.
|