Fig. S4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130123-17
- Publication
- Bosco et al., 2013 - Development of hypothalamic serotoninergic neurons requires Fgf signalling via the ETS-domain transcription factor Etv5b
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
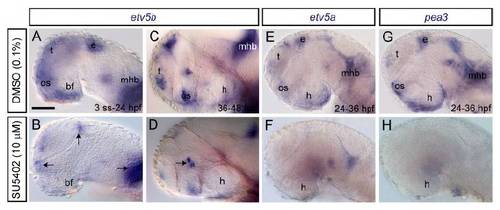
Fgf loss-of-function downregulates expression of pea3 family members. (A-H) Embryos were treated with SU5402 during the developmental stages indicated, fixed directly after treatment and analysed for etv5b, etv5a or pea3 expression (whole-mounts). Following SU5402 treatment, no etv5b transcripts were detected in the basal forebrain (bf), including hypothalamus (h), although transcripts were still detectable in some of the domains normally expressing etv5b, including the telencephalon (t), mid-hindbrain boundary (mhb), optic stalk (os) and pineal/epithalamus (e) (B, arrows) and ventral thalamus (D, arrow). SU5402 treatment also abolished etv5a and pea3 expression in the hypothalamus as well as in other domains where they are normally expressed. Lateral views, anterior left. Scale bar: 50 μm. |