Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-120710-68
- Publication
- Hörndli C.S. et al., 2012 - Sonic hedgehog is indirectly required for intraretinal axon pathfinding by regulating chemokine expression in the optic stalk
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
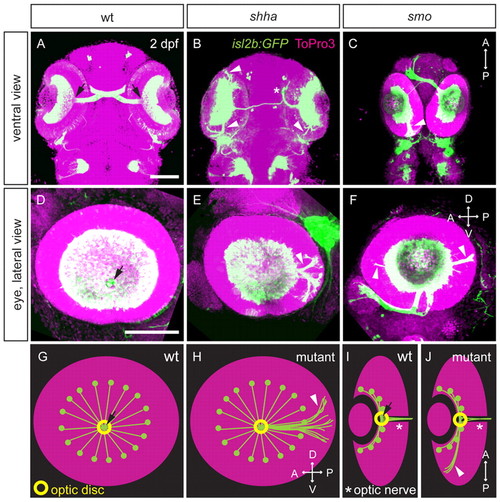
Intraretinal axon pathfinding defects in Hh pathway mutants. (A-J) Retinal projections at 2 dpf in wt, shha and smo zebrafish embryos with isl2b:GFP (green) or isl2b:tagRFP (pseudocolored green in C,F) transgene; nuclei, ToPro3 (magenta). Ventral (A-C) or lateral views (D-F) of maximum-intensity projections and schematics of wt and mutant axon projections showing lateral (G,H) and ventral views (I,J) are shown. In wt embryos (A,D,G,I), RGC axons converge at the optic disc (arrow), where they turn and pass through the optic nerve (I, asterisk). In shha (B,E,H,J) and smo (C,F,H,J) mutants, some axons fail to exit the eye, projecting posteriorly or occasionally anteriorly within the eye (arrowheads). Hh mutants also exhibit misprojections to the ipsilateral optic tectum (asterisk in B). D, dorsal; V, ventral; A, anterior; P, posterior. Scale bars: 100 μm. |