FIGURE
Fig. S9
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-111214-24
- Publication
- Gallagher et al., 2011 - Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. S9
|
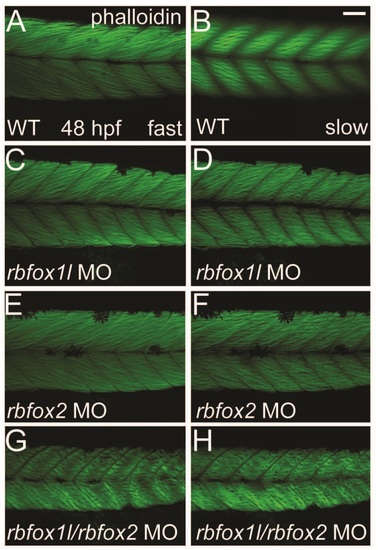
Depletion of Rbfox1l or Rbfox2 alone does not alter the striated appearance of myofibrils. Phalloidin labeling of thin filaments in skeletal muscle of WT embryos reveals normally striated fibers in both fast and slow muscle (A-B). Fiber arrangment of rbfox1l morphants was mildly affected at doses of 9 ng (C-D), whereas rbfox2 morphant fibers had a normal appearance (E-F). In contrast, halved doses of 4.5 ng each of rbfox1l and rbfox2 sbMOs, when co-injected, resulted in highly disorganized, wavy fibers (G-H). Scale bar = 50 µm. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Long-pec |
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 359(2), Gallagher, T.L., Arribere, J.A., Geurts, P.A., Exner, C.R., McDonald, K.L., Dill, K.K., Marr, H.L., Adkar, S.S., Garnett, A.T., Amacher, S.L., and Conboy, J.G., Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions, 251-61, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.