Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-111128-35
- Publication
- Gallagher et al., 2011 - Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
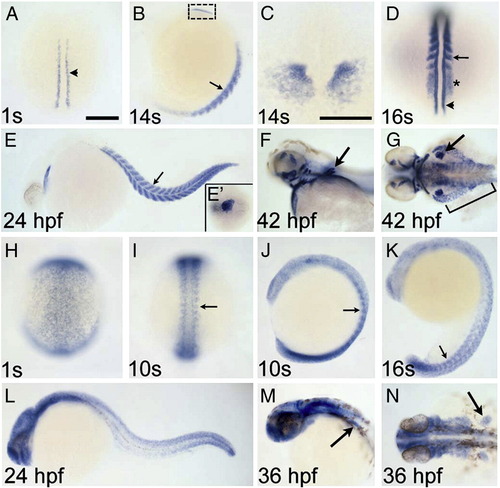
Zebrafish rbfox1l and rbfox2 are expressed in muscle cells. rbfox1l (A–G) and rbfox2 (H–N) expression between the 1-somite stage and 42 hpf are shown in dorsal (A, C, D, G–I, N) and lateral (B, E, F, J–M) views. rbfox1l is expressed in adaxial slow muscle precursor cells (arrowhead in A, D), the anterior presomitic mesoderm (PSM; asterisk in D) and formed somites (small arrows in B, D, E), cardiac mesoderm (B, C, E, E2) and pectoral fin (large arrows in F, G), hypaxial body wall (bracket in G), and head musculature (F, G). rbfox2 is expressed more broadly, with enrichment in the PSM and newly formed somites (small arrows in I–K) at early times (H–N). Strong rbfox2 expression is detected in the tail bud (J–L), but myogenic rbfox2 expression decreases as somites mature (K, L). By 36 hpf, rbfox2 transcripts are detected predominantly in the head and pectoral fin (large arrows in M, N). Panel C is a magnified image, in dorsal view, of the boxed region in B. Scale bar = 200 μm for all panels except C (100 μm). |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | 1-4 somites to High-pec |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 359(2), Gallagher, T.L., Arribere, J.A., Geurts, P.A., Exner, C.R., McDonald, K.L., Dill, K.K., Marr, H.L., Adkar, S.S., Garnett, A.T., Amacher, S.L., and Conboy, J.G., Rbfox-regulated alternative splicing is critical for zebrafish cardiac and skeletal muscle functions, 251-61, Copyright (2011) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.