Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-110720-19
- Publication
- Banerjee et al., 2011 - A novel role for MuSK and non-canonical Wnt signaling during segmental neural crest cell migration
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
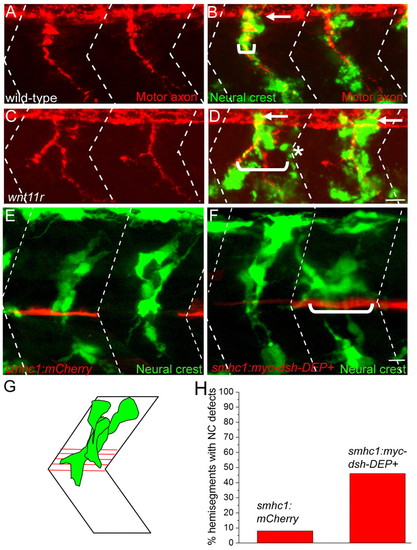
Inhibition of non-canonical Wnt and Dishevelled signaling disrupts neural crest migration. (A-D) Lateral views of 28 hpf wild-type and wnt11r zebrafish embryos stained to reveal neural crest cells (crestin, green) and motor axons (znp1+SV2, red). Arrows point to migrating neural crest cells before they join the path shared with motor axons. In the wnt11r mutant embryo, neural crest cells and motor axons deviate from their central path and migrate over a wider region of the somite (compare brackets in D with B; asterisks mark neural crest cells taking a path independent of motor axons). (E) Stochastic expression of mCherry (red) in slow muscle fibers does not affect neural crest cell (green) migration through the center of the somite. (F) Stochastic expression of Myc-Dsh-DEP+ (red) in slow muscle cells located either at horizontal myoseptum or dorsal to the horizontal myoseptum causes aberrant neural crest cell migration. Neural crest cells in E and F were visualized using Tg(mitfa:GFP)w47. (G) Location of horizontal myoseptum cells used for quantification of the phenotype. (H) Quantification of neural crest migration defect phenotypes. Dashed lines in A-F indicate approximate positions of somite boundaries. Scale bars: 10 μm. |