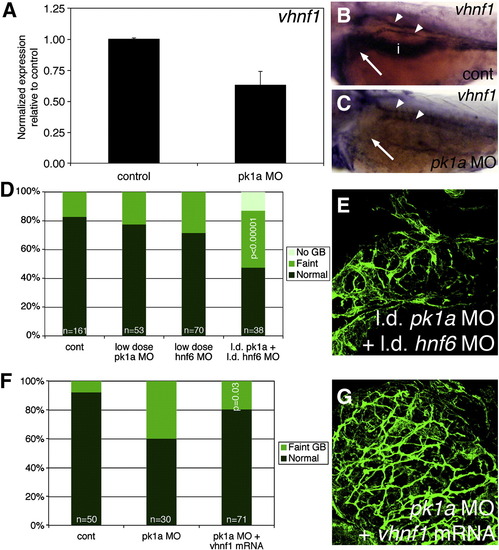
hnf6 and vhnf1 act downstream of PCP in zebrafish biliary development. (A) Quantitative real-time PCR of vhnf1 expression in control and pk1a MO-injected larvae demonstrating a 40% decrease in vhnf1 expression in the morphants. (B, C) In situ hybridizations of 3 dpf control (B, cont) and pk1a MO-injected larvae (C) showing expression of vhnf1 in pronephric ducts in both conditions (white arrowheads), but no expression in the morphant liver (white arrow) or intestine (i). (D) Epistasis experiment demonstrating that knockdown of pk1a and hnf6 is synergistic with respect to an effect on gallbladder PED6 intensity. (E) Confocal projection of cytokeratin immunostaining of livers from 5 dpf larvae injected with the combination of low dose pk1a and hnf6 MOs, showing a pattern of intrahepatic bile ducts similar to that seen after knockdown of pk1a, seen elsewhere. (F) Similar graph of PED6 gallbladder intensity for rescue of pk1a knockdown phenotype by vhnf1 mRNA injection demonstrating improvement in gallbladder intensity (p = 0.03). (G) Confocal projection of cytokeratin immunostaining of livers from 5 dpf larvae injected with pk1a MO with vhnf1 mRNA, demonstrating a pattern similar to control, seen elsewhere.
|

