Fig. 7
|
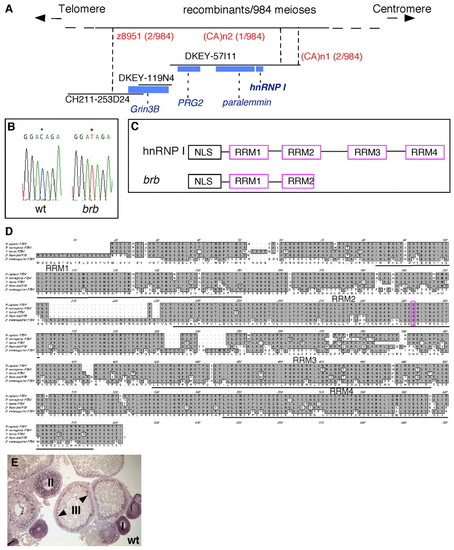
Positional cloning reveals that brom bones encodes the RNA-binding protein, hnRNP I. (A) Genetic/physical map across the brom bones interval on chromosome 2. CH211-253D24, DKEY-119N4 and DKEY-57I11 are three sequenced and overlapping BAC clones in this interval. (CA)n1 and (CA)n2 are polymorphic markers we identified in BAC clone DKEY-57I11. Four transcription units were predicted based on the BAC sequence between z8951 and (CA)n2: grin3b, prg2, paralemmin and hnrnp I. Blue boxes indicate sizes and locations of these genes relative to the BAC clones. (B) Sequencing of wild-type and brom bones alleles revealed a cytosine to thymidine transition (*) in the open reading frame of the hnrnp I gene, which produces a premature stop codon. (C) Schematic diagram showing the protein domain structures of hnrnp I and brom bones. (D) Amino acid sequence alignment of hnRNP I homologs in (top to bottom) human (AAP35465), rat (Q00438), Xenopus (AAF00041), zebrafish (AAH95372) and Drosophila (NP_524703). The residue that is mutated to a stop codon in brom bones (purple) and the RRM domains are highlighted. (E) hnrnp I is expressed during oogenesis as revealed by in situ hybridization on wild-type ovary sections (arrowheads show cortical enrichment in stage III oocytes). |