FIGURE
Fig. S3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080505-27
- Publication
- Matthews et al., 2008 - Directional migration of neural crest cells in vivo is regulated by Syndecan-4/Rac1 and non-canonical Wnt signaling/RhoA
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. S3
|
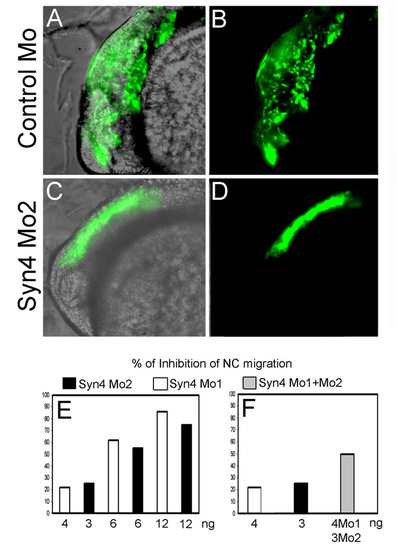
Syn4 is required for NC migration. Migration of NC was examined in vivo using the transgenic zebrafish line sox10:egfp. (A,B) Embryo injected with control MO, showing normal migration of cephalic NC at 24 hpf. (C,D) Embryo injected with syn4 MO2 showing inhibition of NC migration at 24 hpf. The inhibition of NC migration is similar to that produced by syn4 MO1 (see Fig. 5F-J). (E) Dose-dependent effect of syn4 MO1 or MO2 on neural crest migration. (F) The mix of syn4 MO1 + syn4 MO2 has an additive effect on NC migration compared with injection of each single morpholino (n=79). |
Expression Data
| Gene: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Prim-5 |
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development