Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080325-52
- Publication
- Ke et al., 2008 - Combined activity of the two Gli2 genes of zebrafish play a major role in Hedgehog signaling during zebrafish neurodevelopment
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
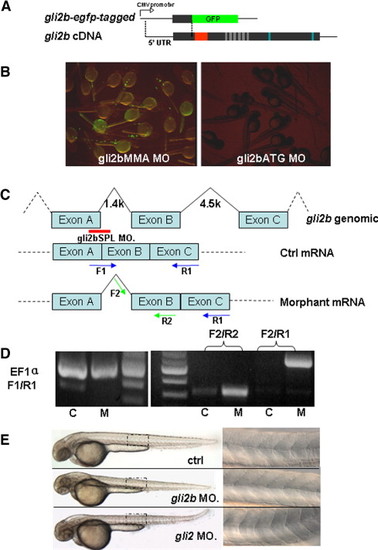
The design and verification of efficiency of anti-Gli2b morpholino. (A) egfp-tagged gli2b construct was made by fusing the fragment containing 5′-untranslated region of gli2b and adjacent region coding the partial N-terminal of Gli2b with egfp coding region. (B) Embryos injected with egfp-tagged gli2b and 4 bp mis-matched control morpholino (gli2bMMA) expressed GFP (left). Embryos co-injected by egfp-tagged gli2b and antisense morpholino (gli2bATG) did not express GFP (right). (C) The diagram shows the strategy of using splicing MO (Red line) for blocking the normal splicing site and organization of predicted mRNA. The blue and green arrows represent the primers for PCR used to evaluate effect of the splicing MO on posttranscriptional processing of gli2b mRNA. (D) RT-PCR using control mRNA (lane C) extracted from gli2bMMS morphants with primers F1/R1 resulted in a band, in contrast to mRNA extracted from gli2bSPL morphant (lane M). However, there were products generated by RT-PCR using morphant gli2bSPL mRNA and prcontrol mRNA (lane C) extracted from gli2bMMS morphants with primers F1/R1 resulted in a band, in contrast to mRNA extracted from gli2bSPL moimers F2/R2 and F2/R1, indicating the successful blocking of proper splicing of exon A and exon B in Gli2b morphants. EF1α primers were used as internal control. (E) Top to bottom: the control morpholino injected embryo, Gli2b morphant, Gli2 morphant. A panel on the right hand side shows the mid-trunk somites at high magnification. The egfp-tagged gli2b-expressing construct was made to test the activity of gli2bATG MO (Fig. S1A). The GFP fluorescence was detected in control morphants after injection of egfp-tagged gli2b construct and 4-bp mis-matched control MO (gli2bMMA). The fluorescence was absent after injection of gli2bATG MO (Fig. S1B). The gli2bSPL MO targets the boundary region of the exon A and adjacent intron (Fig. 1C). When RNA was extracted from gli2bSPL morphants, RT-PCR amplified the fragment predicted for improperly spliced gli2b mRNA (Figs. 1C, D). The fragment corresponding to the normal mRNA (Fig. 1C) was not amplified (Fig. 1D), illustrating high efficiency of MO-mediated mis-splicing of gli2b mRNA. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Prim-15 |
Reprinted from Molecular and cellular neurosciences, 37(2), Ke, Z., Kondrichin, I., Gong, Z., and Korzh, V., Combined activity of the two Gli2 genes of zebrafish play a major role in Hedgehog signaling during zebrafish neurodevelopment, 388-401, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mol. Cell Neurosci.