FIGURE
Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-071228-6
- Publication
- Grzmil et al., 2007 - The INT6 Cancer Gene and MEK Signaling Pathways Converge during Zebrafish Development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
Fig. S1
|
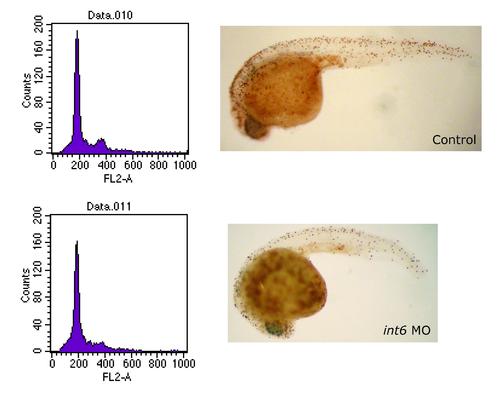
Cell cycle analysis of int6 morphants. Whole-mount immunohistochemistry with the late G2/M phase marker, phospho-histone H3 shows only slightly reduced numbers of cells in late G2/M phase in the int6 morphant compared to the control. Similarly, DNA content as measured by flow cytometry reveals only a slight reduction of cells in G2/M phase in the int6 morphant. Thus, we find that loss of Int6 in normal vertebrate cells (as well as in additional human cancer cell lines, M.G. & C.J.N. unpublished data) does not appear result in an accumulation of cells in G2/M progression. |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ PLoS One