Fig. 8
|
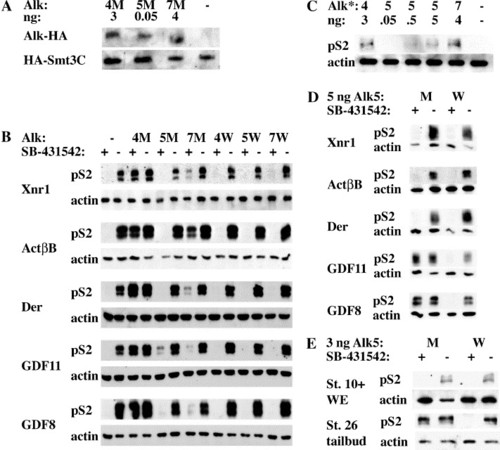
Alk4, Alk5, and Alk7 mediate signaling by different subsets of activin/nodal ligands (A) Embryos were injected with 3 ng Alk4-HA SM (4M), 50 pg Alk5-HA SM (5M), or 4 ng Alk7-SM (7M) along with 500 pg HA-Smt3C as an internal loading control. α-HA IP-Westerns were performed on stage 10.5 embryos. (B) Embryos were injected with 1 ng Xnr1, 20 pg ActβB, 2 ng Derrière, 2 ng cDsl-hGDF11, or 2 ng cDsl-mGDF8 along with 3 ng xAlk4-HA S275M (4M) or WT (4W), 50 pg rAlk5-HA S278M (5M) or WT (5W), or 4 ng rAlk7-HA S270M (7M) or WT (7W). Animal caps were incubated in 100 μM SB-431542 or DMSO until stages 10–10.5, and subsequently harvested for Western blots against p-Smad2. (C) Constitutively active Alks (Alk4*, Alk5*, and Alk7*) were injected at various doses and pSmad2 signaling was assessed in animal caps. (D) 5 ng of rAlk5-HA S278M or rAlk5-HA WT were coinjected with the same concentrations of ligands used in panel A and p-Smad2 signaling was assayed in SB-431542 or DMSO-treated animal caps. (E) Xenopus embryos were injected with 3 ng Alk5-HA S278M or WT. Embryos were treated with 100 μM SB-431542 at stage 6 and harvested at stage 10+, or treated at stage 14 and harvested (tailbud region only) at stage 26. For all experiments, actin was used as a loading control. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 295(2), Ho, D.M., Chan, J., Bayliss, P., and Whitman, M., Inhibitor-resistant type I receptors reveal specific requirements for TGF-beta signaling in vivo, 730-742, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.