Fig. 6
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-051206-3
- Publication
- Maves et al., 2005 - Dynamic and sequential patterning of the zebrafish posterior hindbrain by retinoic acid
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
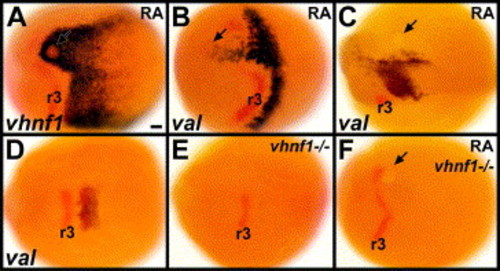
RA induces val expression through vHnf1. (A–C) Embryos with 0.1 mM RA beads placed near the anterior presumptive hindbrain at 6 hpf (shield stage) are stained in red for krox-20 and in blue for vhnf1 at 10.3 hpf (1 s) (A), val at 10.3 hpf (B) or val at 15 hpf (12 s) (C). 13/13 0.1 mM RA beads induced vhnf1 expression unilaterally in the anterior hindbrain, generally surrounding the bead (A). 10/10 0.1 mM RA beads induced val expression unilaterally in the anterior hindbrain (B). (D–F) Wild-type sibling (D), vhnf1 mutant control (E) and vhnf1 mutant embryo with a 0.1 mM RA bead placed near the anterior presumptive hindbrain at 6 hpf (F). Embryos are stained in blue for val and in red for krox-20 at about 11.3 hpf (4 s). 3/8 control vhnf1 mutant embryos showed no val expression; 5/8 showed some weak bilateral val expression (E). RA beads are unable to induce any val expression in vhnf1 mutants (F). 6/9 vhnf1 mutant embryos with RA beads showed no val expression (F); 3/9 showed some very weak bilateral val expression, similar to what is observed in control vhnf1 mutant embryos. 14/14 wild-type sibling embryos with RA beads showed ectopic unilateral val expression. Dorsal views show anterior to the left. Arrows point to beads. r3: rhombomere 3 krox-20 expression. Scale bar: 50 μm. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | 1-4 somites |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 285(2), Maves, L., and Kimmel, C.B., Dynamic and sequential patterning of the zebrafish posterior hindbrain by retinoic acid, 593-605, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.