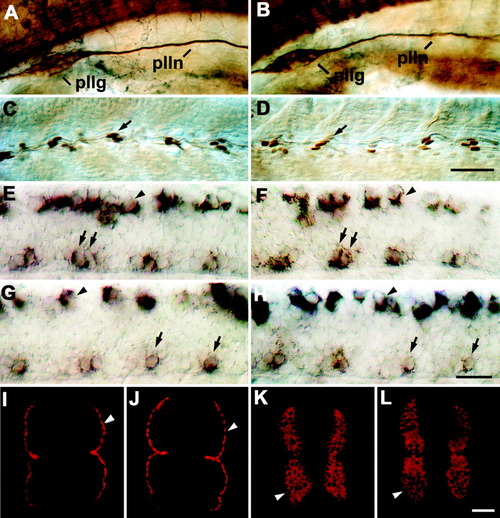
Trunk structures and other axon tracts in 24 hours postfertilization (hpf) embryos are not affected by injection of epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeats RNA. For orientation of A-H, see Figure 1A. In I-L, cross-sections of the trunk are shown (dorsal is up). A-L: Uninjected embryos (A,C,E,G,I,K) were not different from embryos injected with EGF repeats RNA (B,D,F,H,J,L) in tubulin immunohistochemistry (A,B), engrailed immunohistochemistry (C,D), islet-1 (E,F) or islet-2 in situ hybridization (G,H), and F59 (I,J) or F310 (K,L) immunohistochemistry. A,B: The posterior lateral line ganglion (pllg) and nerve (plln) in the anterior trunk region are indicated. C,D: Arrows indicate engrailed immunopositive muscle pioneer cells at the horizontal myoseptum at mid-trunk levels. E-H: In the spinal cord, labeled motor neurons (arrows) and Rohon-Beard cells (arrowheads) are indicated. Islet-1 labels rostral (RoP) and medial (MiP) primary motor neurons. Islet-2 labels caudal primary motor neurons (CaP) and the variably present variable primary motor neurons (VaP). I,J: Arrowheads indicate slow muscle fibers. K,L: Arrowheads indicate fast muscle fibers. Scale bar = 50 μm in D (applies to A-D), 25 μm in H (applies to E-H), 25 μm in L (applies to I-L).
|

