- Title
-
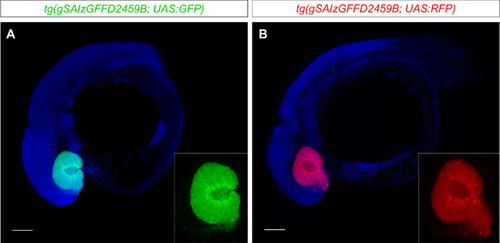
A gal4 insertion in the rx3 locus as a tool for visualization and manipulation of eye fated cells in zebrafish
- Authors
- Vásquez-Ramírez, M.J., Villanueva, A., Lira, E., Nahuelpan, D., Kawakami, K., Valdivia, L.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Biol. Res.
|
|
|
|
|
The |
|
Homozygous |
|
|