- Title
-
Behavioral and molecular insights into anxiety in ube3a and fmr1 zebrafish models of autism spectrum disorders
- Authors
- Dougnon, G., Matsui, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Transl Psychiatry
|
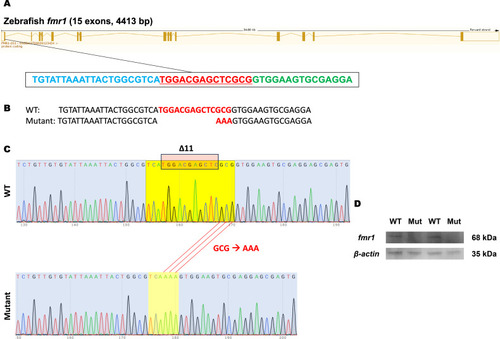
Creation and validation of the ( |
|
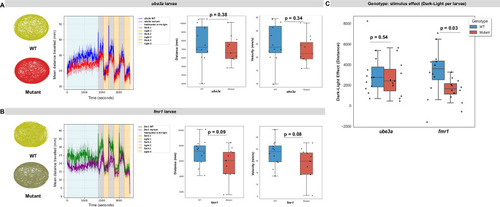
Locomotor activity during the light-dark test (LDT) in larval ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
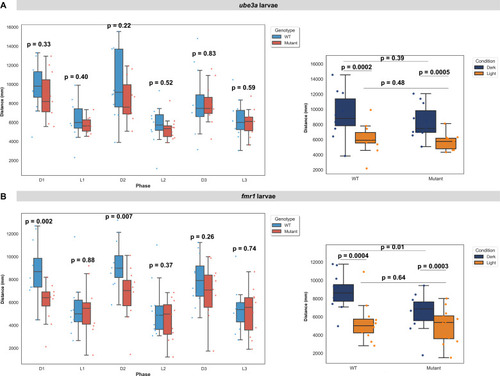
Distances travelled during the light-dark test (LDT) in larval ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
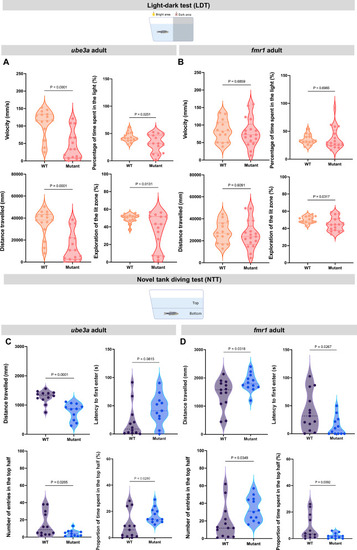
Locomotor and anxiety-related behavior during the LDT and novel tank test (NTT) in adult ( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
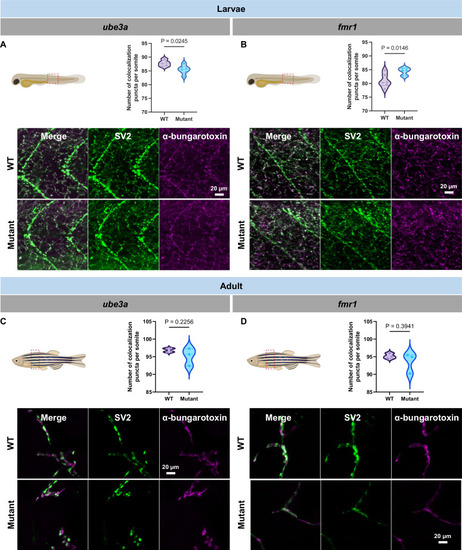
Neuromuscular junction integrity in larvae and adult ( |
|
Comparative expression of potential anxiety and stress-related genes dysregulated in ( |