- Title
-
From in silico screening to in vivo validation in zebrafish - a framework for reeling in the right psychobiotics
- Authors
- Valderrama, B., Daly, I., Gunnigle, E., O'Riordan, K.J., Chichlowski, M., Banerjee, S., Skowronski, A.A., Pandey, N., Cryan, J.F., Clarke, G., Nagpal, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Food Funct
|
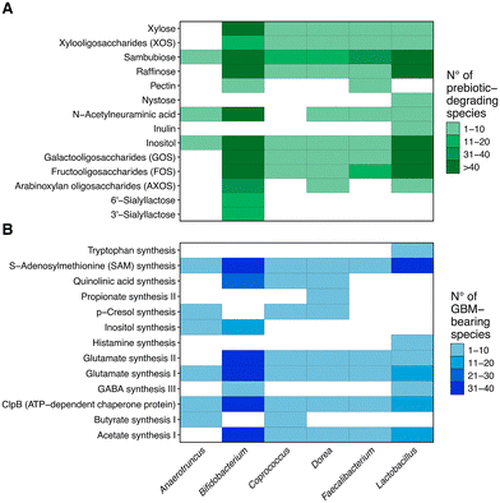
Number of genomes within six genera showing genes encoding for enzymes required for the degradation of carbohydrates of different complexities and involved in the synthesis and degradation of neuroactive molecules. (A) Number of genomes within each genus having at least one gene encoding for a carbohydrate-degrading enzyme. (B) Number of genomes within each genus showing all the genes involved in each GBM, defined as pathways involved in the synthesis of neuroactive molecules. |
|
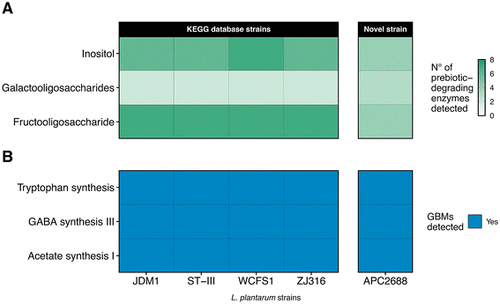
Comparison of carbohydrate-degradation potential and neuroactive potential between four strains of L. plantarum obtained from the KEGG database and the novel strain APC2688. (A) Number of carbohydrate-degrading enzymes identified for each strain (as a gradient of green). (B) Presence or absence of GBMs, defined as pathways involved in the synthesis or degradation of neuroactive molecules. The presence of carbon-degrading enzymes and enzymes involved in the GBMs was inferred from the genomic analysis of the strains. |
|
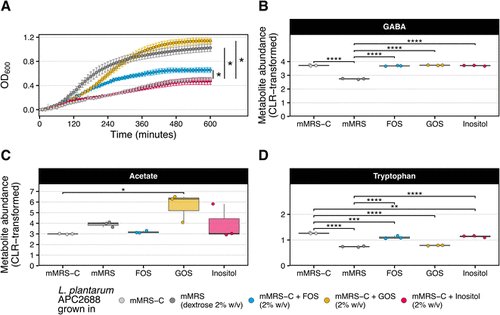
In vitro validation of L. plantarum APC2688 potential to degrade candidate prebiotics of different complexities while producing neuroactive molecules involved in stress modulation. (A) Growth curves of L plantarum APC2688 when growing in different media. An N of three was used for each growth media. (B), (C) and (D) represent the CLR-transformed abundance of GABA, acetate and tryptophan in the cell-free supernatants of APC2688, respectively. An N of three was used for each growth medium. Differences between groups were tested by one-way ANOVA. Stars represent contrasts with adjusted p values below 0.05. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, and ****p ≤ 0.0001. Only statistically significant results are shown. |
|
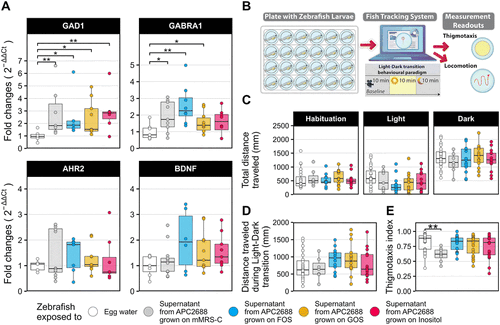
The supernatant of L. plantarum APC2688 grown in media supplemented with the prebiotics induced changes in zebrafish larvae stress response by modulating genes in the GABAergic signalling pathway and altering the larvae behaviour. (A) Expression of genes involved in the anxiety-like behaviour of the zebrafish normalized to the control group (zebrafish treated with egg water). (B) Schematic of the experimental design used in the behavioural paradigm. (C) The total distance travelled during each phase of the behavioural assay. (D) The difference in the total distance travelled during the dark and the light phases used as a measure of anxiety-like behaviour. (E) Thigmotaxis index, which measures the proportion of time each fish spent in the arena's outer zone during the dark phase. Between 5 and 10 samples were used in the gene expression analysis, where a total of 7 to 10 zebrafish larvae were pooled per sample. For behavioural analysis, between 7 and 22 individual fish were used. Differences between groups in panels (A), (C), (D) and (E) were tested using the Kruskal–Wallis test. Contrasts performed in panels (A) and (E) tested differences between the egg water treated group and every other group. Stars represent contrasts with adjusted p values below 0.05. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01. |