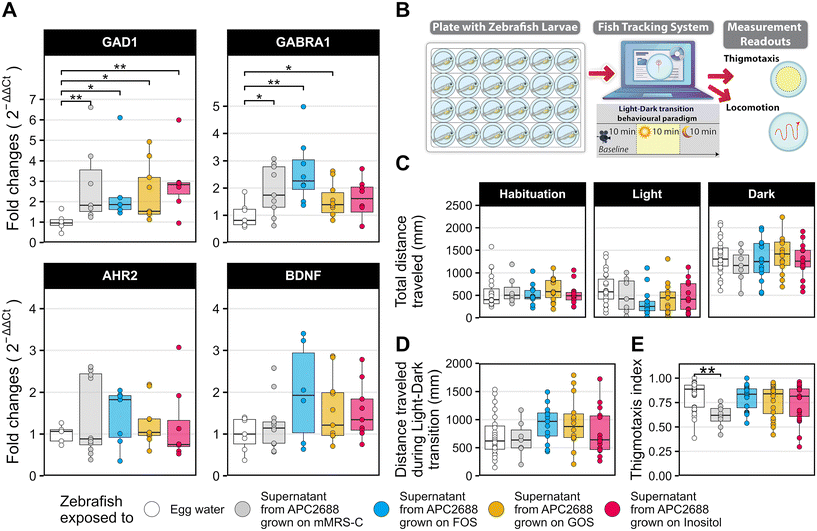
Fig. 4 The supernatant of L. plantarum APC2688 grown in media supplemented with the prebiotics induced changes in zebrafish larvae stress response by modulating genes in the GABAergic signalling pathway and altering the larvae behaviour. (A) Expression of genes involved in the anxiety-like behaviour of the zebrafish normalized to the control group (zebrafish treated with egg water). (B) Schematic of the experimental design used in the behavioural paradigm. (C) The total distance travelled during each phase of the behavioural assay. (D) The difference in the total distance travelled during the dark and the light phases used as a measure of anxiety-like behaviour. (E) Thigmotaxis index, which measures the proportion of time each fish spent in the arena's outer zone during the dark phase. Between 5 and 10 samples were used in the gene expression analysis, where a total of 7 to 10 zebrafish larvae were pooled per sample. For behavioural analysis, between 7 and 22 individual fish were used. Differences between groups in panels (A), (C), (D) and (E) were tested using the Kruskal–Wallis test. Contrasts performed in panels (A) and (E) tested differences between the egg water treated group and every other group. Stars represent contrasts with adjusted p values below 0.05. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Food Funct