- Title
-
Oscillatory DeltaC Expression in Neural Progenitors Primes the Prototype of Forebrain Development
- Authors
- Nian, F.S., Liao, B.K., Su, Y.L., Wu, P.R., Tsai, J.W., Hou, P.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Mol. Neurobiol.
|
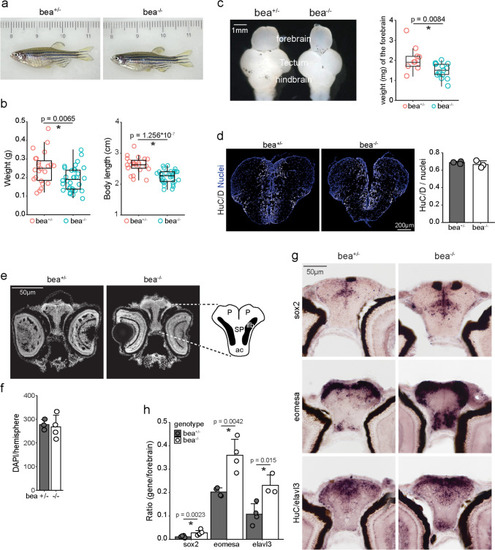
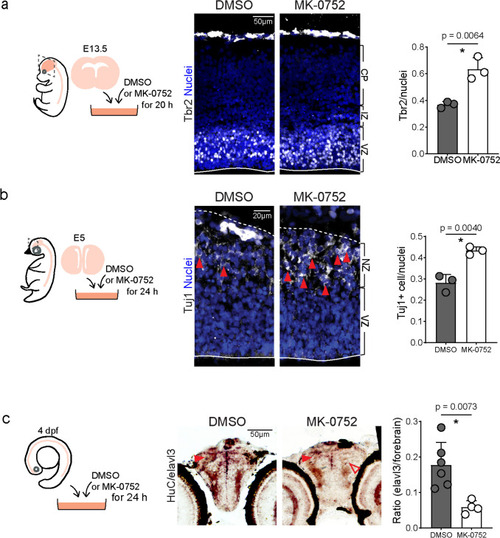
Increased neurons and progenitors in the forebrain of |
|
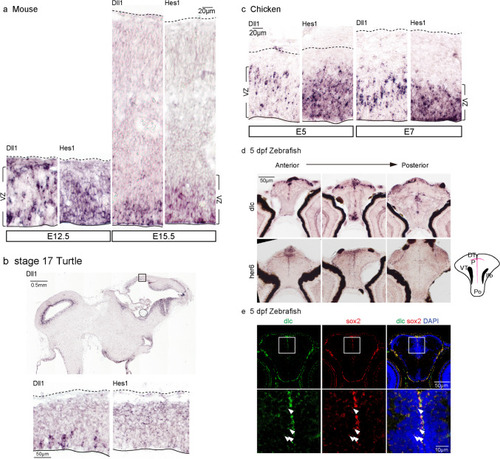
Expression pattern of |
|
|
|
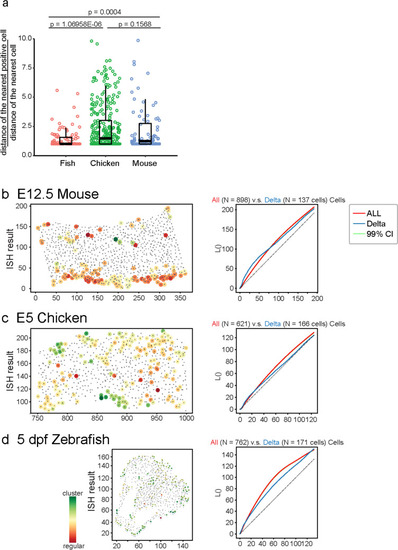
Fluctuating dlc expression was not synchronized in the developing forebrain of larval zebrafish. |
|
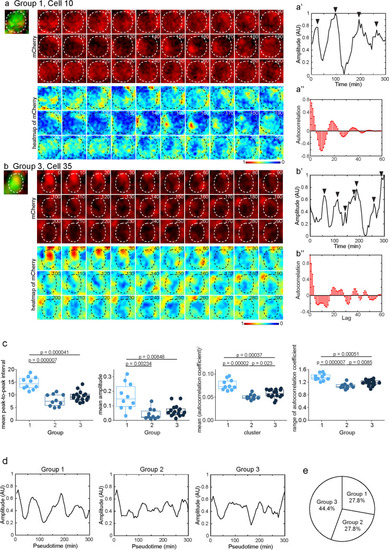
Blocking Notch signaling increased neural precursor numbers in developing mouse and chicken dorsal telencephalon but not in the larval zebrafish forebrain. |