- Title
-
Constitutively active CaMKII Drives B lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma in tp53 mutant zebrafish
- Authors
- Rothschild, S.C., Lai, G., Tombes, R.M., Clements, W.K.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
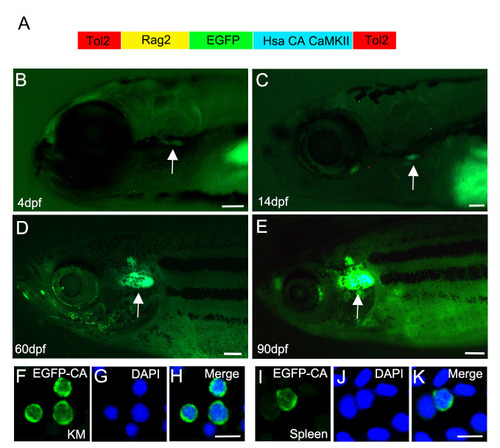
Transgenic expression of human (Hsa) constitutively active (T287D, CA) EGFP-CA-CaMKII in lymphocytes of zebrafish. |
|
(A-F) |
|
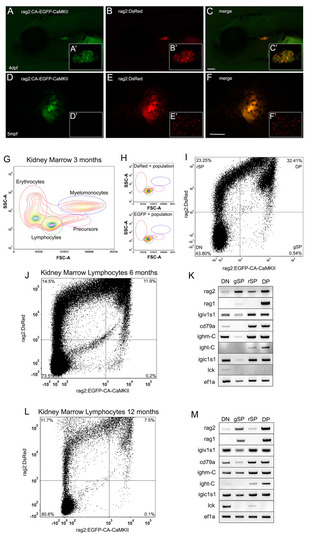
The lymphocyte population is expanded in the kidney marrow of FACS analysis of the kidney of six-month old |
|
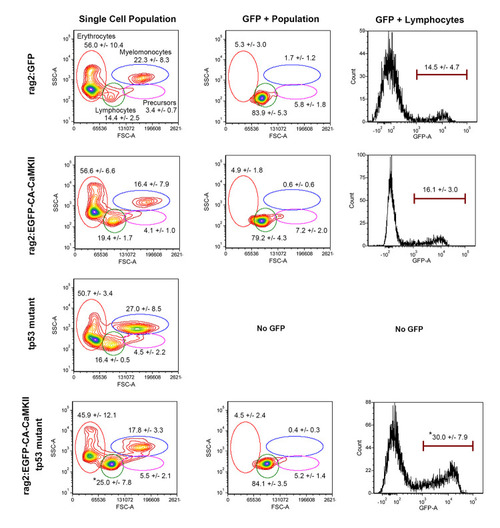
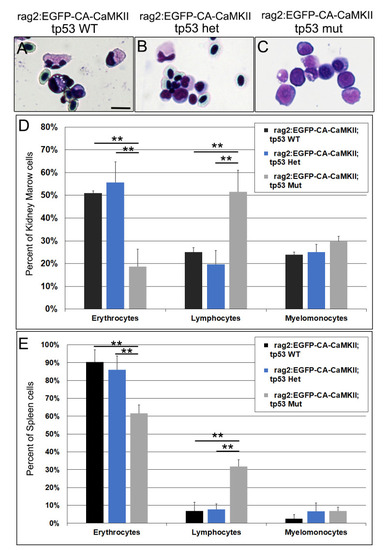
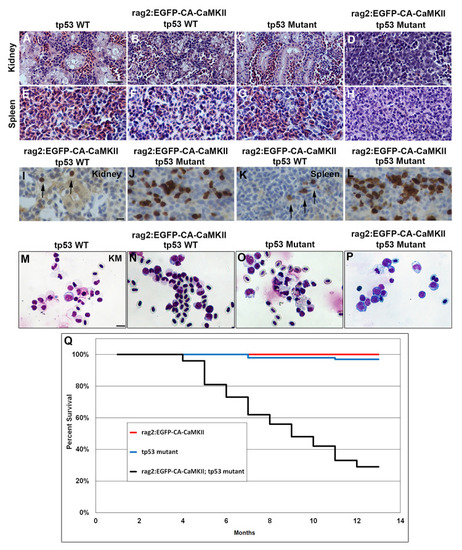
Lymphocytes are significantly expanded in the kidney marrow and spleen of Lineage distributions as determined by cell morphology in the (A-D) kidney marrow and (E) spleen of 9–12 month old fish segregated into |
|
Hematoxylin and eosin stained sections of the (A-D) head kidney and (E-H) spleen of nine month old (A, E) wild type, (B, F) |
|
Kidney marrow blasts expressing EGFP positive and negative lymphoid cells from the kidney marrow were sorted from six-nine month old adult |
|
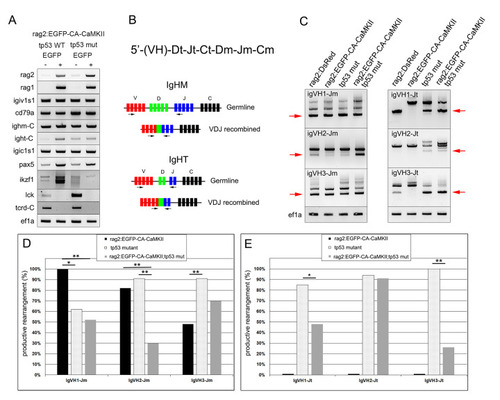
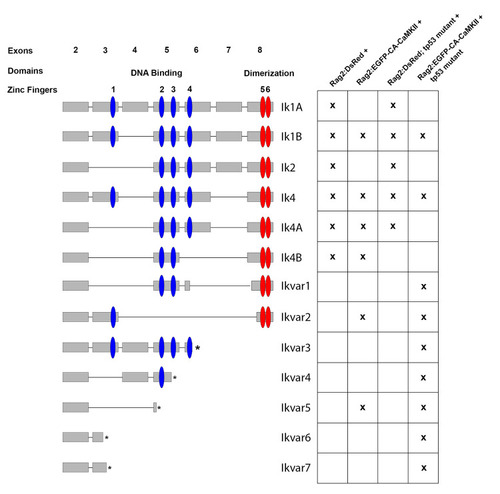
Izf1 splicing is altered in rag2:EGFP-CA-CaMKII;tp53 mutant B cells. Zebrafish |
|
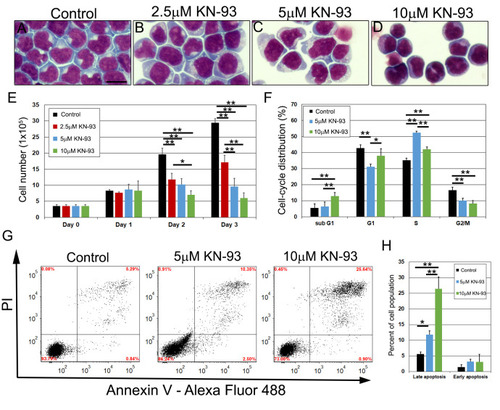
HEMA3 stained NALM6 cells treated with 2.5μM, 5μM, and 10μM KN-93 at 48h (A-D). NALM6 growth curves were assessed at 24-hour intervals until 72h after KN-93 treatment. (E, n = 3). Cell cycle distribution was assessed after PI staining in control, 5μM, and 10μM KN-93 treated NALM6 cells at 48h (F, n = 5). NALM6 cells were stained with Annexin V and PI after KN-93 treatment and analyzed using flow cytometry at 48h. The lower left quadrant are cells that are negative for Annexin V and PI, the upper left quadrant is PI positive only indicative of necrosis, the upper right quadrant identifies cells that are positive for both Annexin V and PI indicating late apoptosis, and the bottom right quadrant shows cells that are Annexin V positive, which indicates early stages of apoptosis (G). The bar graph shows the percent of cells that are in early and late stage of apoptosis from four experiments (H). P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey HSD. * p<0.05 and ** P<0.01. Scale bar: 20 μm in A. |