- Title
-
A zebrafish model of Ifih1-driven Aicardi-Goutières syndrome reproduces the interferon signature and the exacerbated inflammation of patients
- Authors
- Bernal-Bermúdez, B., Martínez-López, A., Martínez-Morcillo, F.J., Tyrkalska, S.D., Martínez-Menchón, T., Mesa-Del-Castillo, P., Cayuela, M.L., Mulero, V., García-Moreno, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Immunol
|
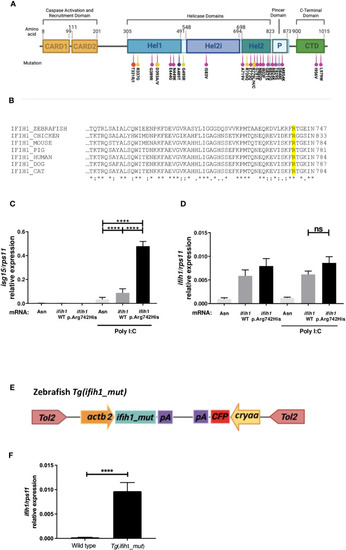
Localization, sequence alignments, |
|
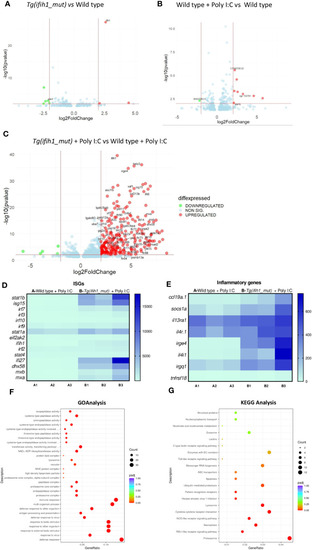
Transcriptomic analysis of the |
|
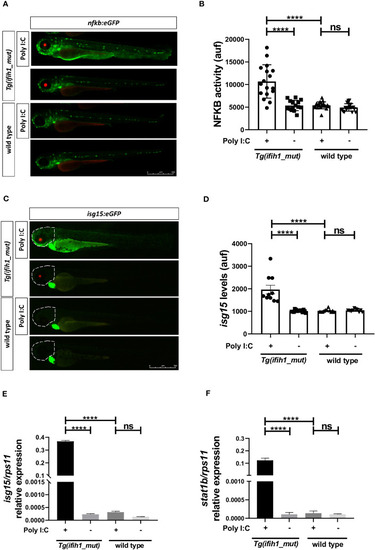
Real-time visualization of inflammation and type I IFN induction in |
|
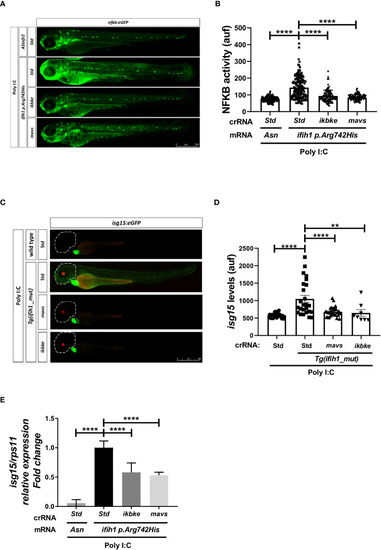
Genetic inhibition of Mavs/Ikbke signaling pathway impairs the induction of inflammation and ISGs in |
|
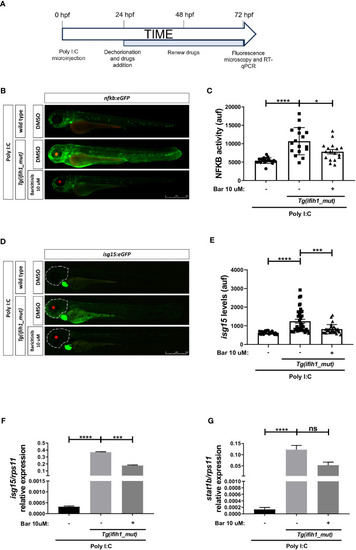
Pharmacological inhibition of Jak impairs the induction of ISGs and inflammation in |
|
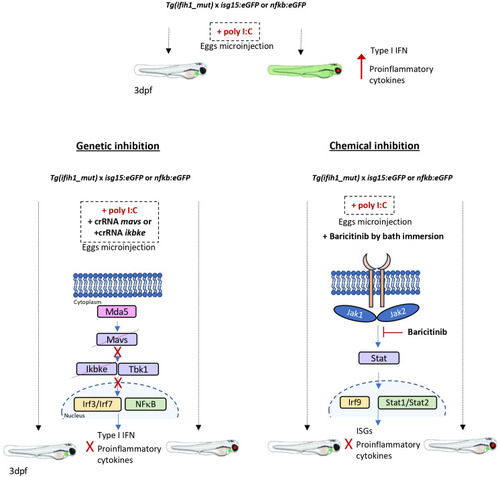
Schematic summary. |