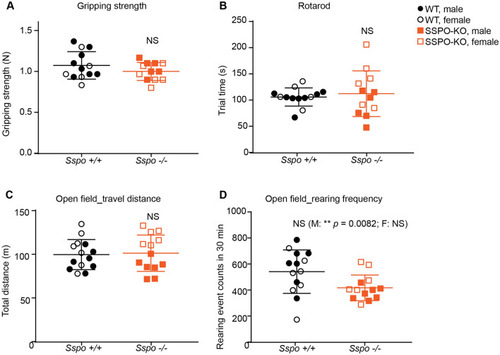
Sspo-deficiency does not alter basic motor tasks in 12–14 week old adult mice. No behavioral differences were observed in Sspo−/− mice compared to wild type littermate controls in A forelimb gripping strength (not significant, N = 13 wild type, 8 males and 5 females, N = 12 Sspo−/−, 6 males and 6 females, p = 0.20), B average time spent on the rotarod (not significant, N = 13 wild type, 8 males and 5 females, N = 12 Sspo−/−, 6 males and 6 females, p = 0.64), C total distance traveled during each 30 min (not significant, N = 14 wild type, 7 males and 7 females, N = 13 Sspo−/−, 7 males and 6 females, p = 0.83). open-field test, and D number of rearing events during each 30 min (N = 14 wild type, 7 males and 7 females, N = 13 Sspo−/−, 7 males and 6 females, p = 0.0262 (significant p with Sidak correction for multiple comparison in open field test is 0.0170). If analyzing males only, ** p = 0.0082). Open field test. All panels have male and female marked separately and analyzed together unless specified. Welch’s t-test
|