- Title
-
Hindbrain rhombomere centers harbor a heterogenous population of dividing progenitors which rely on Notch signaling
- Authors
- Belmonte-Mateos, C., Meister, L., Pujades, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol
|
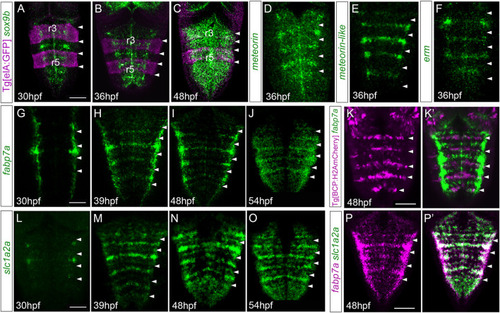
Hindbrain rhombomere centers display a specific combination of gene expression. |
|
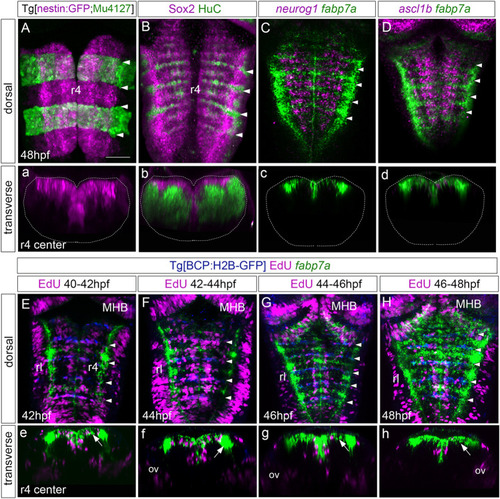
Rhombomere centers harbor proliferating neural progenitors. |
|
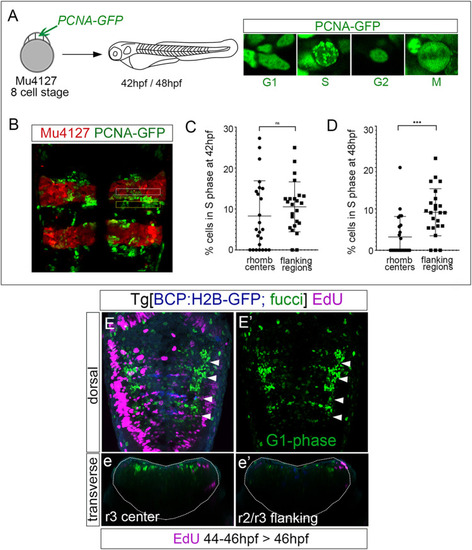
Rhombomere centers harbor G1-phase-arrested progenitors. |
|
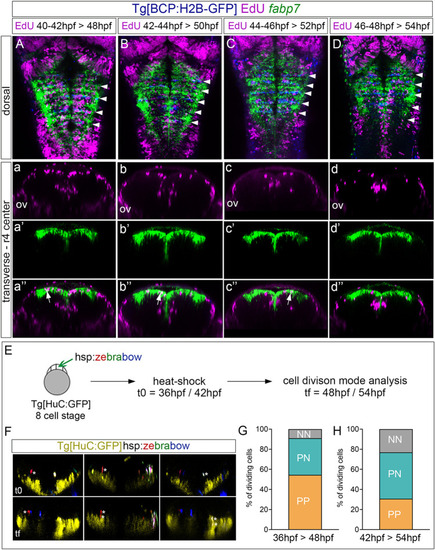
Proliferating progenitor cells within the rhombomere centers shift their division mode over time. |
|
Rhombomere centers display Notch activity. |
|
Progenitor cells in the rhombomere centers are Notch-responsive. Wild-type embryos were treated with either DMSO |
|
|