- Title
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis β-lactamase variant reduces sensitivity to ampicillin/avibactam in a zebrafish-Mycobacterium marinum model of tuberculosis
- Authors
- van Alen, I., Aguirre García, M.A., Maaskant, J.J., Kuijl, C.P., Bitter, W., Meijer, A.H., Ubbink, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Sci. Rep.
|
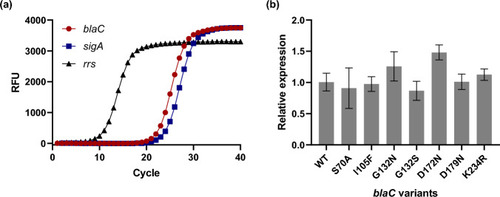
Expression of Mtb |
|
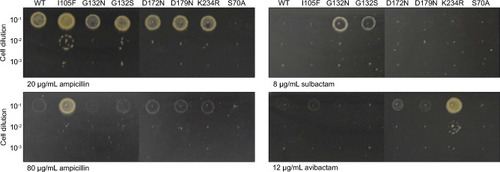
Activity of Mtb BlaC mutants produced in Mmar |
|
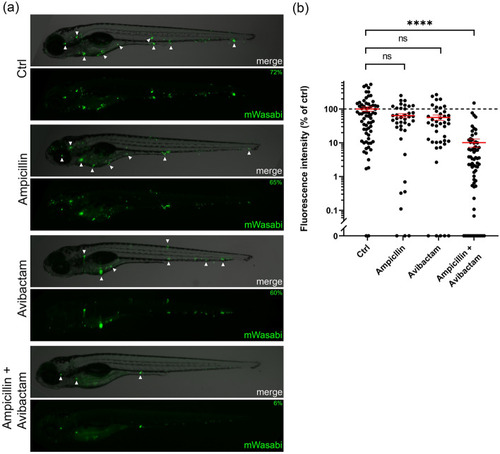
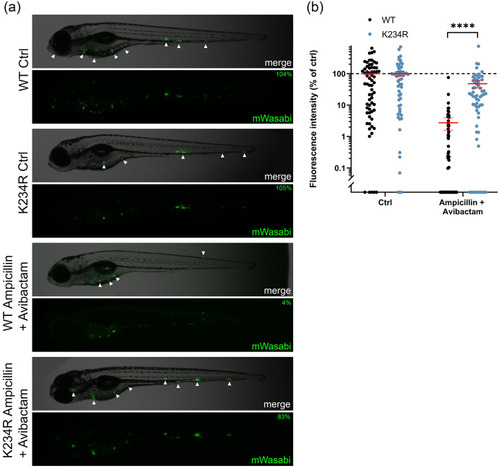
Effect of combination treatment on zebrafish embryos infected with mWasabi-labelled Mmar producing Mtb BlaC at 4 dpi. ( |
|
Effect of combination treatment on zebrafish embryos infected with mWasabi-labelled Mmar producing Mtb BlaC variants at 4 dpi. ( |