- Title
-
Connectivity Mapping Using a Novel sv2a Loss-of-Function Zebrafish Epilepsy Model as a Powerful Strategy for Anti-epileptic Drug Discovery
- Authors
- Zhang, Y., Heylen, L., Partoens, M., Mills, J.D., Kaminski, R.M., Godard, P., Gillard, M., de Witte, P.A.M., Siekierska, A.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Mol. Neurosci.
|
|
|
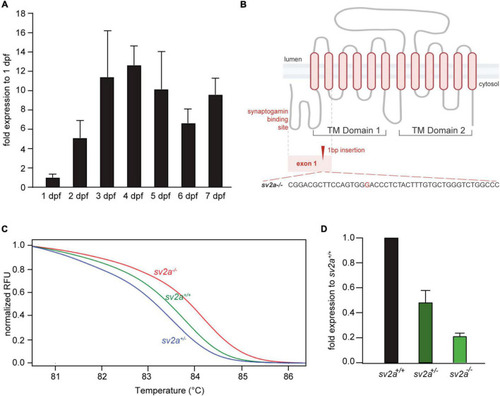
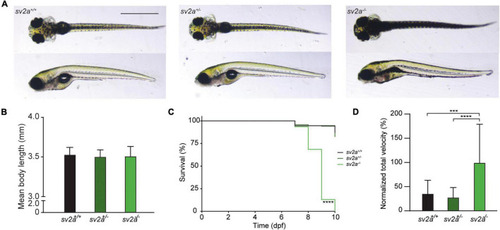
Morphological, survival and behavioral analysis of |
|
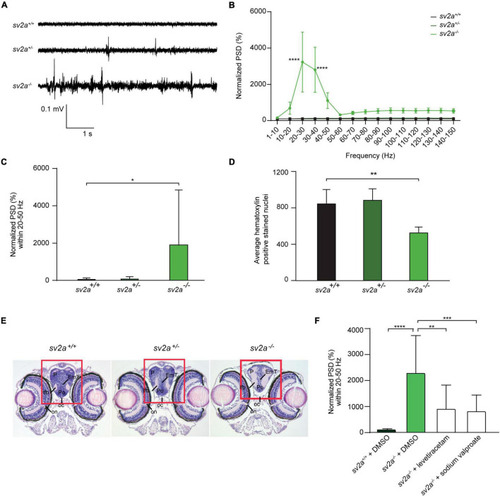
Spontaneous electrographic seizures and brain malformation in PHENOTYPE:
|
|
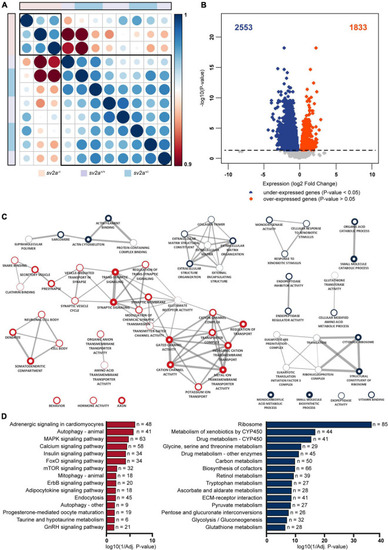
Transcriptome analysis and gene ontology (GO) enrichment map of |
|
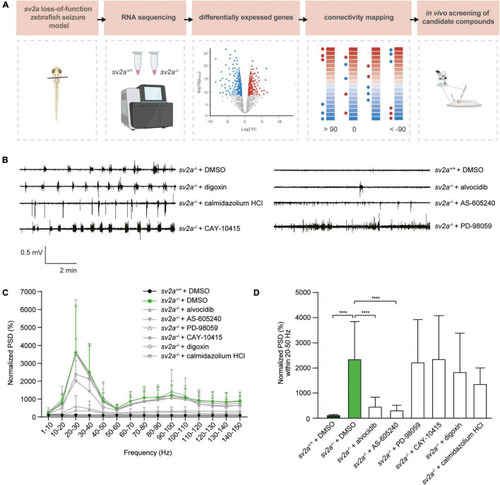
Connectivity mapping in PHENOTYPE:
|