- Title
-
Dopamine Homeostasis Imbalance and Dopamine Receptors-Mediated AC/cAMP/PKA Pathway Activation are Involved in Aconitine-Induced Neurological Impairment in Zebrafish and SH-SY5Y Cells
- Authors
- Zhou, J., Peng, C., Li, Q., Yan, X., Yang, L., Li, M., Cao, X., Xie, X., Chen, D., Rao, C., Huang, S., Peng, F., Pan, X.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Pharmacol
|
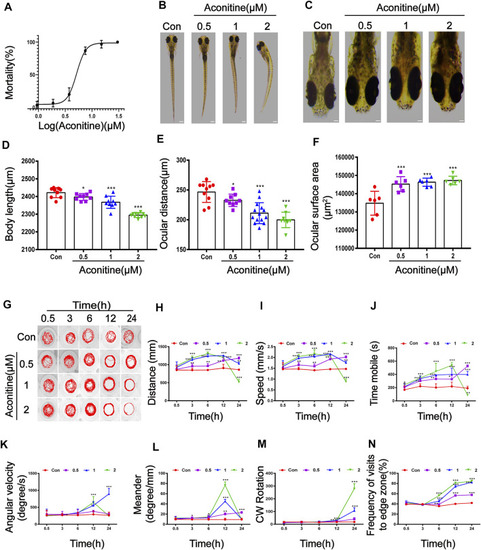
Morphological and swimming behavior changes of zebrafish larvaes after aconitine exposure. |
|
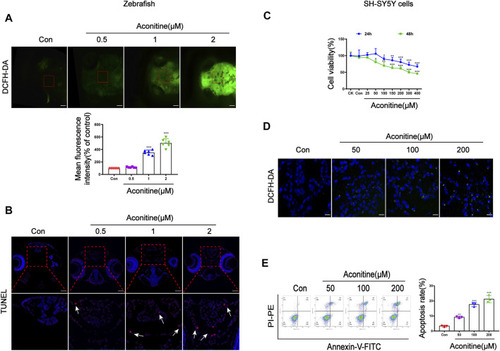
Cell damage of zebrafish larvaes and SH-SY5Y cells caused by aconitine. |
|
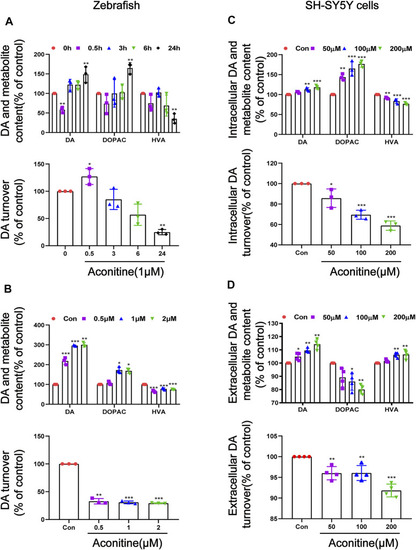
Alteration of dopamine and its metabolites levels in zebrafish larvaes and SH-SY5Y cells after aconitine exposure. |
|
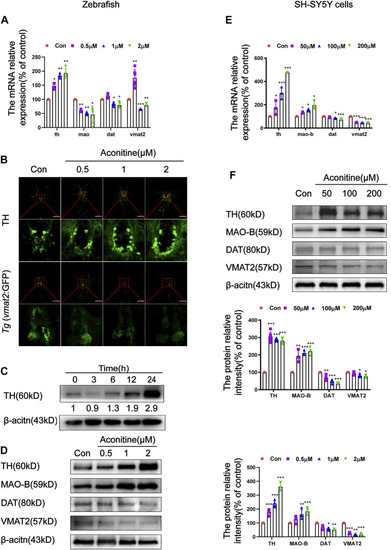
Effects of aconitine on TH, MAO, DAT and VMAT2 expressions in zebrafish larvaes and SH-SY5Y cells. |
|
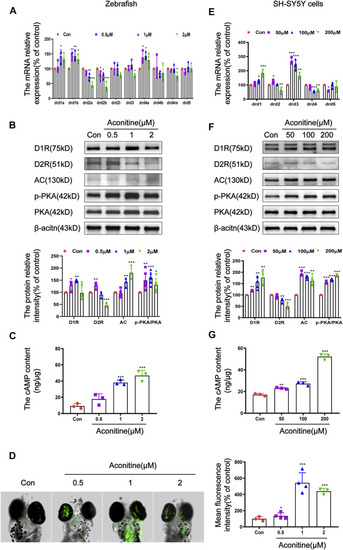
Regulation of DR-mediated AC/cAMP/PKA signalling pathway by aconitine in zebrafish larvaes and SH-SY5Y cells. |
|
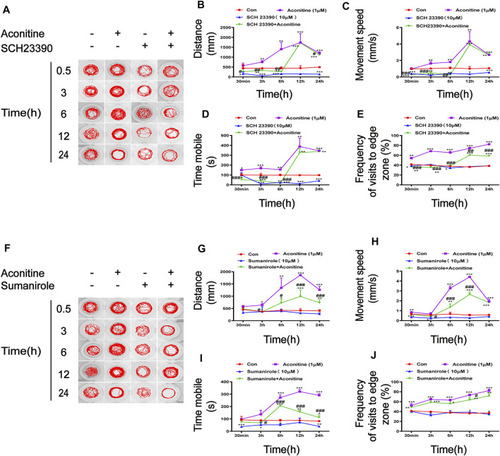
FIGURE 6. Effects of SCH23390 and sumanirole on behavioral changes induced by aconitine in zebrafish larvaes. (A–E) SCH23390 inhibited aconitine-stimulated excitatory behaviors, n = 10. (F–J) Sumanirole suppressed aconitine-induced excitatory behaviors, n = 10. The values are expressed as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. control groups. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. aconitine-treated groups. |
|
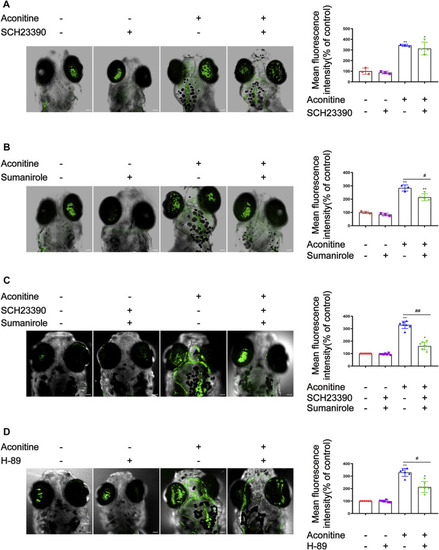
Effects of SCH23390, sumanirole and H-89 on intracellular Ca2+ changes induced by aconitine in zebrafish larvaes. |
|
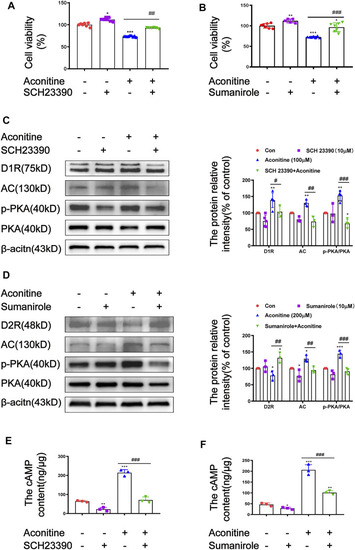
FIGURE 8. Effects of SCH23390 and sumanirole on aconitine-induced the activation of AC/cAMP/PKA pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. (A–B) SCH23390 and sumanirole inhibited aconitine-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells, respectivevly, n = 9. (C–F) SCH23390 and sumanirole suppressed aconitine-mediated the activation of AC/cAMP/PKA pathway, n = 5. The values are expressed as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. control groups. #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. aconitine-treated groups. |
|
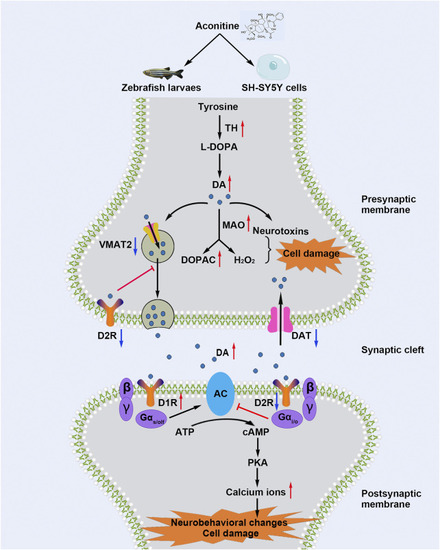
Schematic diagram shows that aconitine induces neurological impairment via dopamine homeostasis disruption and dopamine receptors-mediated AC/cAMP/PKA pathway activation in zebrafish larvaes and SH-SY5Y cells. |