- Title
-
Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba dropping pills in Parkinson's disease
- Authors
- Yu, D., Zhang, P., Li, J., Liu, T., Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., Zhang, J., Lu, X., Fan, X.
- Source
- Full text @ J Pharm Anal
|
The 12 main constituents of Ginkgo biloba dropping pill (GBDP) and EGb 761. Data were analyzed using Student’s t-test, ∗P < 0.05. |
|
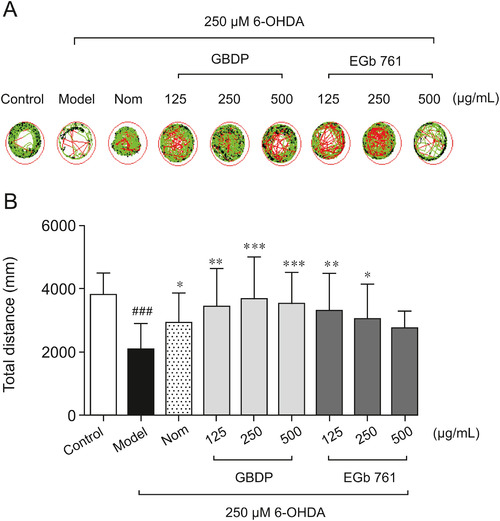
GBDP rescued 6-hydroxy-dopamine (6-OHDA)-induced locomotor impairment in zebrafish. (A) A Viewpoint Zebrabox system was used to test locomotive behavior. The green plot and the red line represent the movement trajectories recorded by the Viewpoint Zebrabox system. (B) Total distance travelled in 30 min. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. ###P < 0.0001, compared with the control group; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗P < 0.0001, compared with the 6-OHDA group. n = 10 per group. Nom indicates the positive control nomifensine-treated group. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
GBDP protected against 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic neuron loss in zebrafish. (A) Representative images of DA neurons in the zebrafish brain, indicated by tyrosine hydroxylase immunostaining. Red arrow: dopaminergic neurons in the zebrafish brain. (B) The area of the dopaminergic neurons calculated for each group. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. ###P < 0.0001, compared with the control group; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.001 compared with the 6-OHDA group. n = 10 per group. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
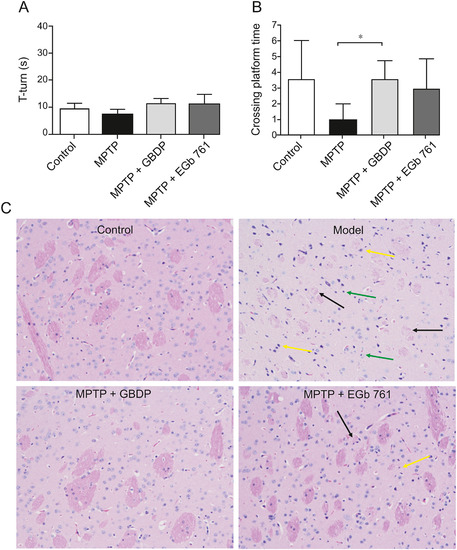
GBDP improves 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced cognitive impairment in mice. (A) T-turn time in the pole test on day 19. (B) Site crossings in the morris water maze (MWM) test. (C) GBDP protected dopaminergic neurons in the MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain sections were processed for HE staining. Black arrow: nerve fiber bundles are loose and lightly stained and the fiber components are significantly reduced; yellow arrow: a large number of neurons were atrophied and the nuclei were intensely stained; green arrow: glial cells show slight hyperplasia. ∗∗P < 0.001. Data were analyzed by unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test. n = 5 per group. |
|
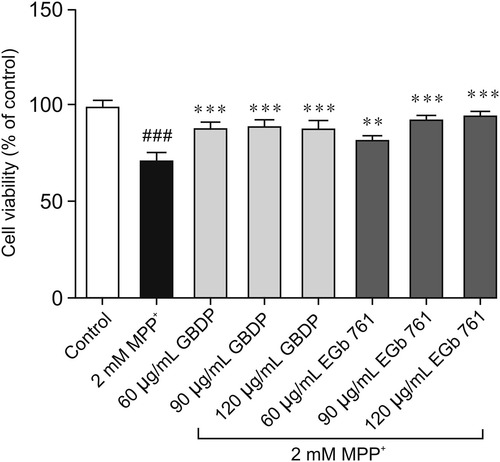
GBDP protected SH-SY5Y cells against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-pyridinium (MPP+)-induced toxicity. GBDP and EGb 761 protected SH-SY5Y cells against the MPP+-induced decrease in cell viability. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. ###P < 0.0001, compared with the control group; ∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗P < 0.0001, compared with the MPP+ group. n = 3 per group. |
|
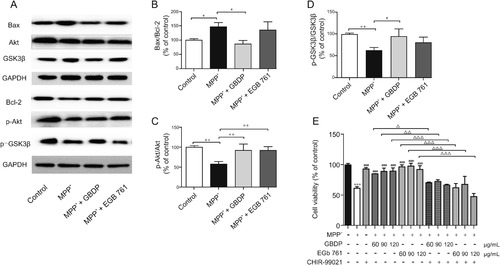
GBDP treatment decreased the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and increased Akt/GSK3β levels in MPP+-treated human SH-SY5Y cells. (A) Western blot assay of p-Akt, Akt, p-GSK3β, GSK3β, Bax, and Bcl-2. (B–D) Ratio of p-Akt, Akt, p-GSK3β, GSK3β, Bax, and Bcl-2 band intensities. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.001. (E) SH-SY5Y cells were pre-treated with the GSK3β inhibitor, CHIR-99021 (10 μM) for 2 h and subsequently exposed to 2 mM MPP+ and different concentrations of GBDP or EGb 761. After 24 h, cells underwent an MTT assay. ∗∗∗P < 0.0001, compared with the control group. ###P < 0.0001, compared with the MPP+ group. △P < 0.05, △△P < 0.001, △△△P < 0.0001. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. n = 3 per group. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. |