- Title
-
The multi-dimensional embryonic zebrafish platform predicts flame retardant bioactivity
- Authors
- Truong, L., Marvel, S., Reif, D.M., Thomas, D., Pande, P., Dasgupta, S., Simonich, M.T., Waters, K.M., Tanguay, R.L.
- Source
- Full text @ Reprod. Toxicol.
|
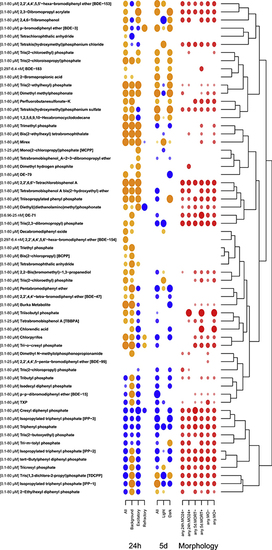
Dot-heatmap representation of the developmental toxicity for 61 FRCs.
Dechorionated embryos were exposed to 61 FRCs to 4 dosing regimens from 6 to 120 hpf. The size of the dots represents potency, with the bigger circles representing a lower concentration; color dots represent morphological endpoints (red), while neurobehavioral endpoints are represented as yellow (hyperactivity) and blue (hypoactivity). The lowest effect concentration was computed for each endpoint in the morphology, 24h (24 hpf photomotor response), and 5d (120 hpf larval photomotor response) behavioral assays. For morphology, summary endpoints were created: any 24hr sublethal effect (any24h.MO24−), any 24 hr effect (any24h.MO24+), any 120 hpf sublethal effects (any.5d.MORT−), any 120 effects (any.5d.MORT+), any sublethal effects (any.MO−) and any effect throughout the exposure (any.MO+). The 24 hr behavioral assay detects motion in 3 intervals, Background, Excitatory, and Refractory, and a summary endpoint (all). At 5d, the behavioral assay measures distance traveled in the visible light phase and the dark (infrared) phase, and overall movement (All). |
|
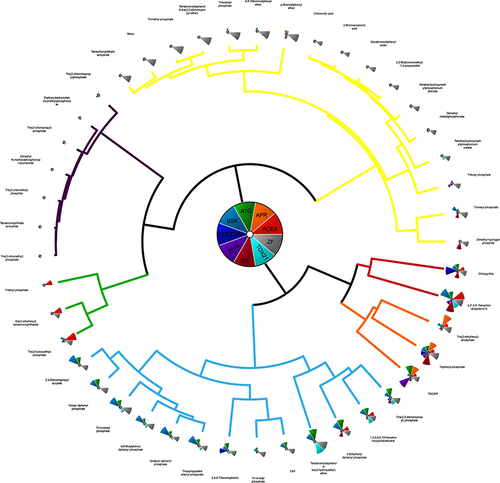
Clustering of 45 FRCs assessed in ToxCast assays.
From the 61 FRCs, 45 were previously assessed in 8 vendor groups that are part of the ToxCast or Tox21 program and also in zebrafish. The vendor’s data are visualized as a slice of the pie (OT; Odyssey Thera NVS: Novascreen; CEETox; BSK: BioSeek; ATG: Attagene; APR: Apredica; ACEA, Tox21 assays in the Tox21 consortium toolbox, ZF: this study zebrafish). |
|
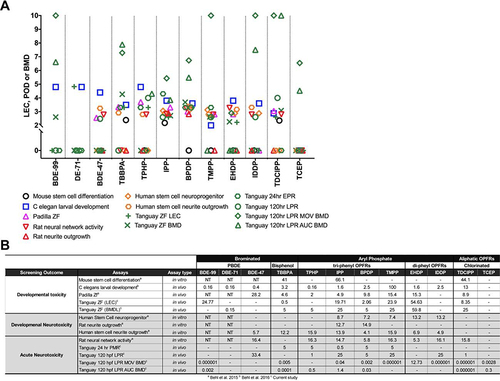
Comparison of flame retardant toxicity to other high throughput assays.
The lowest effect concentration (LEC), point of departure (POD), and benchmark dose (BMD) for 12 FRC that were previously assessed in in vitro models, zebrafish and C. elegans. (A) The LEC and POD across the 11 assays are plotted for the 12 FRCs (–log10 (value/1000,000)) with the higher the value, the more potent. (B) The 11 assays are broken up into 3 screening outcomes (developmental toxicity, developmental neurotoxicity, and acute neurotoxicity) and the LEC/POD expressed in μM is listed per FRC class. Dash (−) represents no toxicity observed at the tested concentrations. NT denotes FRCs not tested in certain assays. For the zebrafish behavior assay, the values in the bracket represent the phase the LEC/POD was calculated. |
|
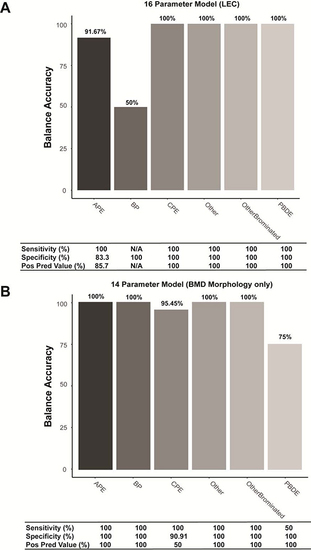
Classification modeling performance.
We used RandomForest to build a classification model for 6 FRC classes: Other, OtherBrominated, PolyBrominated Diphenyl Ether (PBDE), aryl phosphate ester (APE), brominated phenol (BP), and chlorinated phosphate ester (CPE). The balanced accuracy (BA) for each of the FRC classes, and their sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value for the models (A) 16 parameters of 13 chemicals with the LEC for all 3 zebrafish assays and (B) 14 parameters with the BMD for the zebrafish morphology only. Both models yield a BA of 91.67%. |
Reprinted from Reproductive toxicology (Elmsford, N.Y.), 96, Truong, L., Marvel, S., Reif, D.M., Thomas, D., Pande, P., Dasgupta, S., Simonich, M.T., Waters, K.M., Tanguay, R.L., The multi-dimensional embryonic zebrafish platform predicts flame retardant bioactivity, 359-369, Copyright (2020) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Reprod. Toxicol.