- Title
-
Pharmacological restoration of visual function in a zebrafish model of von-Hippel Lindau disease
- Authors
- Ward, R., Ali, Z., Slater, K., Reynolds, A.L., Jensen, L.D., Kennedy, B.N.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
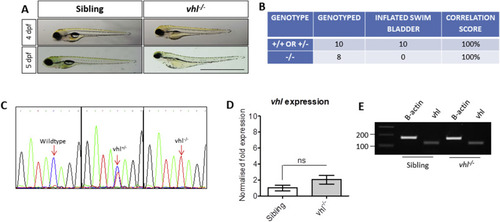
Characterisation of vhl−/− zebrafish. A) Gross morphology of 4 and 5 dpf vhl larvae highlighting the absence of a swim bladder, plus yolk and pericardial oedema in vhl-/- larvae. Scale bar = 2 mm. B) Phenotype-Genotype correlations in offspring generated from vhl ± incrosses. DNA sequencing of PCR amplicons from genomic DNA confirmed a positive correlation between swim bladder uninflation and vhl−/− genotype. This strategy was used to select vhl−/− larvae for all further experimentation. C) Sequencing chromatograms illustrating the single nucleotide polymorphism (C > T) in the vhl sequence resulting in a premature STOP codon. D) Real time PCR analysis of vhl expression in vhl−/− larval eyes in comparison to siblings (+/− or +/+). ns = not significant when p < 0.05. E) Reverse transcriptase PCR highlighting vhl expression in vhl−/− and sibling eyes at 5 dpf. |
|
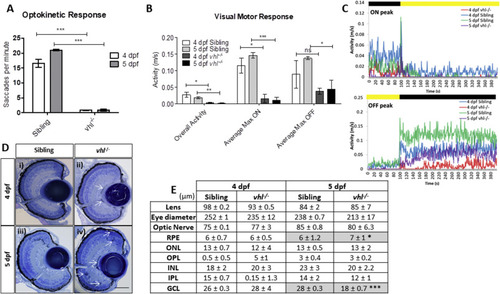
vhl−/− larvae display retinal abnormalities and impaired visual function. vhl−/−larvae possess A) reduced visual capacity in response to a moving striped stimulus (OKR) n = 3, 12 technical replicates per treatment group per experiment. B) reduced movement in response to changes in light intensity (VMR) and C) VMR chromatographs illustrating average max ON/OFF peaks. n = 3, 12 technical replicates per treatment group per experiment. D) vhl−/− larvae display defects in retinal arrangement at 5 dpf. Representative light microscopy images of retinal sections from i) 4 dpf sibling control, ii) 4 dpf vhl−/− iii) 5 dpf sibling control and iv) extensive retinal damage, thought to be fluid accumulation present in 5 dpf vhl−/− larvae (white arrows). Scale bar = 50 μm. E) Morphometric analysis based on 3 independent measurements from 3 larvae per group. Values represent mean ± standard deviation of retinal layer thickness in μm. No statistically significant differences is observed between retinal layers of sibling and vhl−/− at 4 dpf. The retinal layers analysed include Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE), Outer Nuclear Layer (ONL), Outer Plexiform Layer (OPL), Inner Nuclear Layer (INL), Inner plexiform Layer (IPL) and Ganglion Cell Layer. |
|
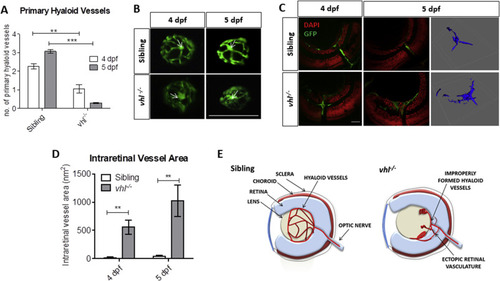
vhl−/− zebrafish larvae possess ocular vascular abnormalities at 4 and 5 dpf. A) Primary hyaloid vessel number at 4 and 5 dpf. vhl−/− larvae highlight a significant reduction in hyaloid branches at 4 and 5 dpf compared to sibling control. Data is representative of 3 biological replicates. N = 10 larvae per group per biological replicate. B) Fluorescent images of fli1:EGFP hyaloid vessels on sibling and vhl−/- dissected lenses at 4 and 5 dpf. White arrows illustrate central point from which primary branches are quantified. Scale bar = 200 μm. C) Confocal imaging revealed abnormal retinal neovascularisation (white arrows) at 4 and 5 dpf through the inner plexiform layer (IPL) and ganglion cell layer (GCL) compared to sibling control. Z-stacks confirmed aberrant vessel growth (blue) through the retina. Scale bar = 20 μm. D) Intraretinal vessel area is significantly increased in vhl−/− at both 4 and 5 dpf. N = 5 larvae per group E) Schematic of proposed ocular blood vessel formation in vhl−/− zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf. |
|
Sunitinib malate significantly improves visual function and reduces VEGF expression in vhl−/− larvae. A) Gross morphology of sibling and vhl-/- larvae treated with increasing doses of sunitinib malate at 5 dpf. Treatment reduces yolk and cardiac oedema but does not result in swim bladder inflation. B) All concentrations of sunitinib tested increase OKR visual function at 5 dpf with 1 μM sunitinib malate highlighting a statistically significant improvement. n = 3, 12 technical replicates per experiment. C) Correlation between hyaloid vessel number and visual function in 5 dpf wildtype larvae treated with sunitinib malate. n = 3 with 10 technical replicates per experiment. Dotted line denotes vhl−/− visual function and number of primary hyaloid branches at 5 dpf. D) VMR Max ‘ON’ response is significantly increased dose dependently in larvae treated with 0.2 μM and 0.5 μM Sunitinib. n = 3, 12 technical replicates per treatment group per experiment. E) VMR chromatograms illustrating the average Max ON and Max OFF peaks after treatment. F) Expression of pro- and anti-angiogenic vhl−/− larval eyes following sunitinib treatment. |
|
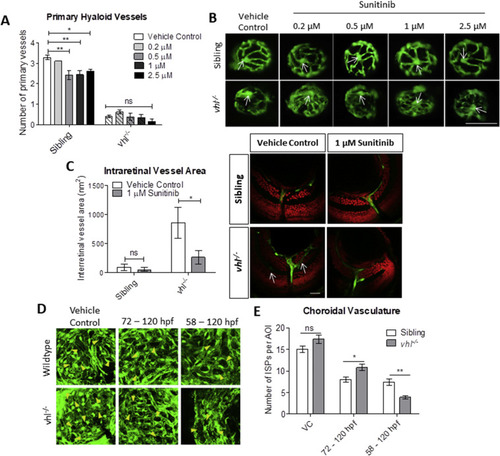
Sunitinib malate improves hyaloid vessel patterning, reduces retinal neovascularisation and inhibits excessive development of the choriocapillaris in vhl−/− larvae. A) Treatment from 58 hpf does not significantly increase vhl−/− primary hyaloid vessel number at 5 dpf. B) Representative images highlighting an overall improvement of vessel patterning following treatment with sunitinib from 58 hpf. White arrows denote central point from which primary blood vessels are counted. n = 3, 12 technical replicates per group per experiment. C) Reduction of ectopic intraretinal vasculature following treatment with 1 μM sunitinib. White arrows highlighting ectopic intraretinal vessels. Quantification of n = 5 larvae per treatment group. Scale bar = 20 μm. D) Z-stack projections of the sub-retinal choriocapillaris vasculature (endothelial cells shown in green) of Tg(fli1:EGFP) or vhl−/−(fli1:EGFP) at 120 hpf following treatment for 72 or 48 h as indicated. Yellow arrowheads point to interstitial pillars (ISPs). E) Quantification of the number of interstitial pillars per area of interest (AOI). n = 10 larvae. PHENOTYPE:
|
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 457(2), Ward, R., Ali, Z., Slater, K., Reynolds, A.L., Jensen, L.D., Kennedy, B.N., Pharmacological restoration of visual function in a zebrafish model of von-Hippel Lindau disease, 226-234, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.