- Title
-
Dynamic Tissue Rearrangements during Vertebrate Eye Morphogenesis: Insights from Fish Models
- Authors
- Cavodeassi, F.
- Source
- Full text @ J Dev Biol
|
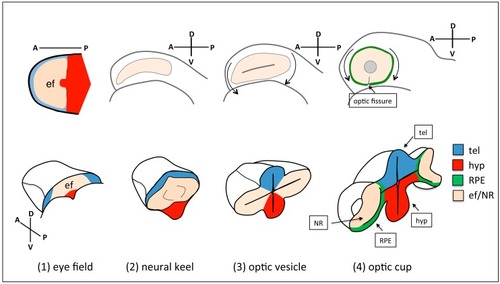
Schematic of eye morphogenesis in zebrafish. Eye field specification in the anterior portion of the neural plate (ANP) ( |
|
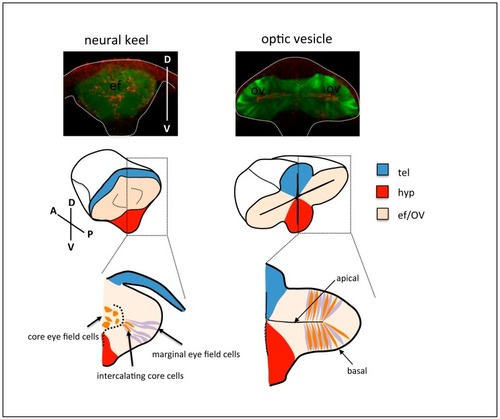
Top row: frontal views of neural keel ( |
|
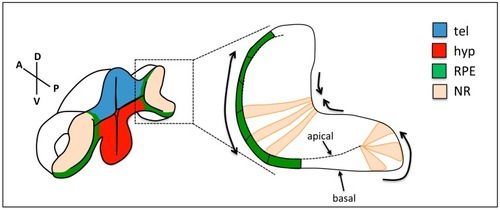
Changes in cell shape during optic cup folding. Prospective retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells (green) flatten, cells at the rim show apical constriction and basal lamellipodia, and neural retina (NR) cells show basal constriction. Arrows show the expected direction of tissue movement. tel: telencephalon; hyp: hypothalamus; RPE: retinal pigment epithelium; NR: neural retina. |