- Title
-
Restoration of anatomical continuity after spinal cord transection depends on Wnt/β-catenin signaling in larval zebrafish
- Authors
- Wehner, D., Becker, T., Becker, C.G.
- Source
- Full text @ Data Brief
|
The spinal cords structurally reconnect after transection in zebrafish larvae. A-C) Intraspinal injection of fluorescent dextran into the rostral end of the spinal cord distributes to the whole spinal cord tissue, including neuropil and central canal, along the entire rostro-caudal axis. Shown is a lateral view of a whole mount larva (A) and transverse sections through the larva at different positions along the rostro-caudal axis (B-C). Approximate positions of the sections are indicated in the cartoon. D-H) Distribution of intraspinally injected dextran at different time points post-lesion. Fluorescent dextran injection fails to label spinal cord tissue caudal to the lesion site in freshly lesioned animals and at 1 dpl (D). At 2 dpl 33% of dextran-injected larvae show spinal cord labeling caudal to the lesion site (arrow), which further increases to 74% at 3 dpl, indicating restoration of spinal tissue continuity (D). Asterisk indicates lesion site. Fischer's exact test: ***P<0.001, n.s. indicates not significant. E) Transverse section of a 1 dpl larva shows absence of dextran labelling of spinal cord tissue caudal to the lesion site. F) Transverse section of a 3 dpl larva shows dextran labeling of spinal cord tissue caudal to the lesion site. G) Transverse section through the lesion site immediately after lesion shows dextran labelling of tissue surrounding the spinal cord. H) Transverse section through the lesion site at 3 dpl shows that dextran labelling is largely confined to regenerated spinal cord tissue. Approximate positions of the sections are indicated in the cartoon. A-H) Views are lateral (A, D; dorsal is up, rostral is left) or transversal (sections in B-C, E-H; dorsal is up). Abbreviations: BF, brightfield; Rhod. Dextran, Rhodamine dextran; cc, central canal. Scale bars: 250 µm (A), 200 µm (D), 25 µm (B-C, F), 20 µm (E, G-H). Error bars indicate s.e.m. |
|
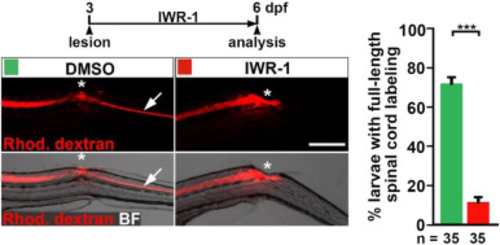
Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibits dye spreading towards the caudal transected spinal cord. Pharmacological inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway (IWR-1 treatment) reduces the proportion of animals with dextran transport beyond the spinal lesion site, indicating lack of restored spinal continuity (Fischer's exact test: ***P<0.001). In DMSO-treated control larvae, intraspinally injected fluorescent dextran is transported across the lesion site (asterisk) into the caudal spinal cord (arrow). Dextran transport is interrupted at the level of the lesion site (asterisk) in IWR-1-treated larvae. Shown is a lateral view, dorsal is up, rostral is left). Abbreviations: BF, brightfield; Rhod. Dextran, Rhodamine dextran. Scale bar: 200 µm. Error bars indicate s.e.m. |