- Title
-
The Control of Calcium Metabolism in Zebrafish (Danio rerio)
- Authors
- Lin, C.H., Hwang, P.P.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.
|
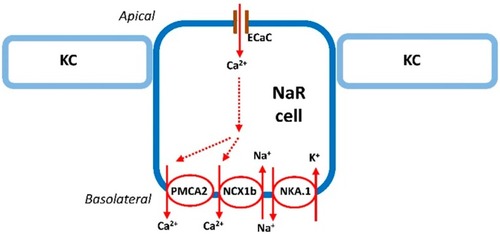
Na+-K+-ATPase-rich cell (NaRC) in zebrafish. Details of the transport pathways refer to the text (“The mechanism of Ca2+ uptake in zebrafish” section). ECaC, epithelial Ca2+ channel; KC, keratinocyte; NCX1b, Na+/Ca2+ exchanger 1b; NAK.1, Na+-K+-ATPase α1 subunit subtypes (atp1a1a.1); NaRC, Na+, K+-ATPase-rich cell; PMCA2, plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase 2. Solid and dashed arrows, the route of Ca2+ transport in NaRC. |
|
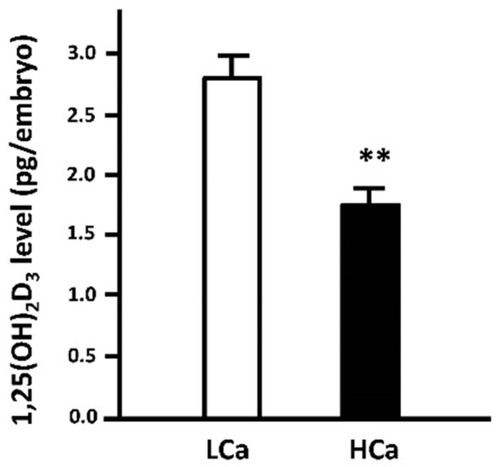
Effect of environmental Ca2+ concentrations on whole-body 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25(OH)2D3) content in 3 day post-fertilization (dpf) zebrafish embryos. One to two cell-stage zebrafish embryos were incubated in low- (0.02 mM Ca2+) and high-Ca2+ (2.0 mM Ca2+) water, respectively, for three days. The low-Ca2+ (LCa) group showed a higher level of 1,25(OH)2D3 than the high-Ca2+ (HCa) group. Whole-body 1,25(OH)2D3 content was measured with an ELISA kit (E0467GE, EIAlab, Wuhan, China). Values are the mean ± SEM ( |
|
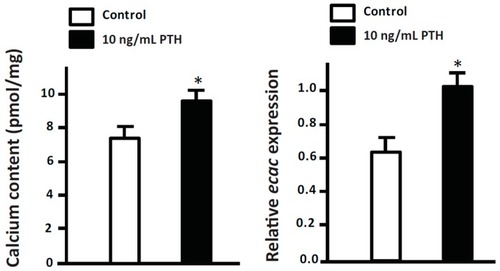
Effect of human parathyroid hormone (PTH) amide on whole-body ECaC mRNA expression and calcium content in 3-dpf zebrafish embryos. One to two cell-stage zebrafish embryos were treated with 10 ng/mL human PTH 1-34 amide (H-5964, BACHEM, Torrance, CA, USA) for three days. The treatment of human PTH 1-34 amide resulted in significant increases in calcium content and ECaC mRNA expression. Whole-body Ca2+ content was measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. mRNA expression was analyzed by qPCR using the primer sets in the study by previous study [ |
|
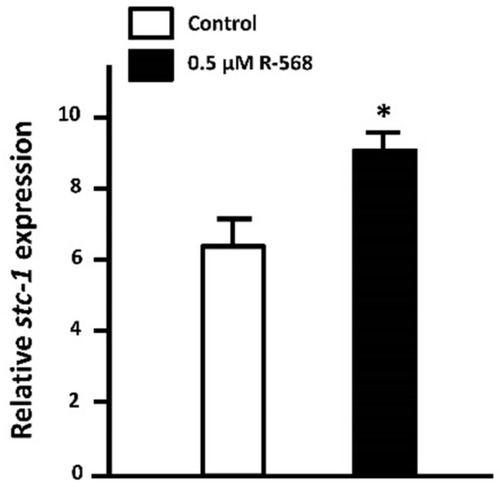
Effect of activated calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) on STC-1 mRNA expression in 3-dpf zebrafish embryos. Zebrafish embryos at 3-dpf were treated with 0.5 µM R-568 (sc-361302, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA) for 8 h. The treatment of R-568 significantly stimulated STC-1 mRNA expression. mRNA expression was analyzed by qPCR using the primer sets in the study by previous study [ |
|
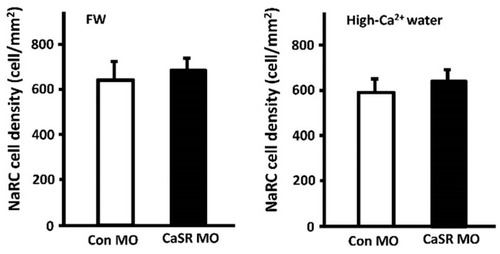
Effect of CaSR knockdown on the density of NaRCs in 3-dpf zebrafish embryos. CaSR and control morpholinos (CaSR and Con MO) [ |
|
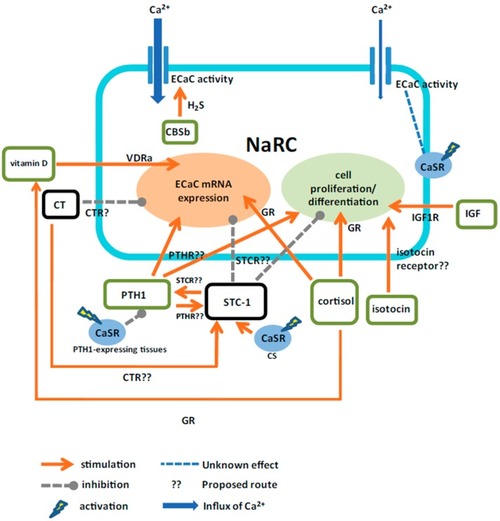
A proposed model for the actions of calcitropic hormones on zebrafish NaRCs. Calciotropic hormones are suggested to directly and indirectly (via the effector hormone(s)) regulate the cell proliferation/differentiation and the mRNA expression or activity of ECaC in NaRCs. CaSR, calcium-sensing receptor; CBSb, cystathionine-β-synthaseb; CS, corpuscle of Stannius; CT, calcitonin; CTR, calcitonin receptor; ECaC, epithelial Ca2+ channel; GR, glucocorticoid receptor; H2S, hydrogen sulfide; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; NaRC, Na+-K+-ATPase-rich cell; PTH1, parathyroid hormone 1; PTHR, parathyroid hormone receptor; STC-1, stanniocalcin1; STCR, stanniocalcin receptor; VDRa, vitamin D receptor A. |