- Title
-
A high-throughput fluorescence-based assay system for appetite-regulating gene and drug screening
- Authors
- Shimada, Y., Hirano, M., Nishimura, Y., and Tanaka, T.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
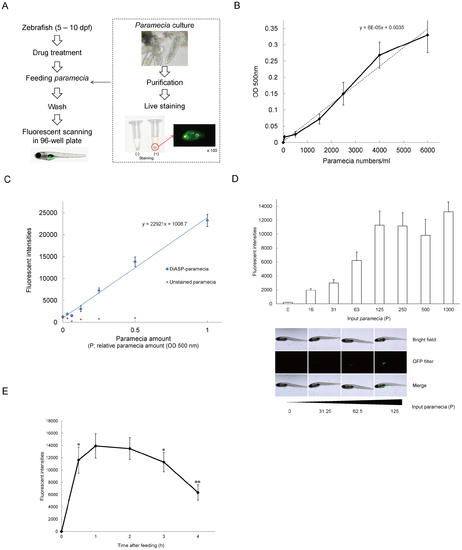
Zebrafish feeding assay using 4-Di-10-ASP labeled paramecia. (A) Schematic representation of the feeding assay. (B) The actual numbers of paramecia correlated with optical density at 500 nm (OD500). (C) Correlation between the relative amount of paramecia (P) and fluorescent intensity. (D) Fluorescent intensities of ingested paramecia in zebrafish. The fluorescent intensities of paramecia in zebrafish abdomen increased independently to the numbers of introduced-paramecia. All values are mean ± SEM, n = 15. (E) Fluorescent intensities after free-feeding of 4-10-Di-ASP-labeled paramecia. Fluorescent intensities of ingested paramecia were at maximum levels 1-3 h after feeding. All values are mean ± SEM, n = 15, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with 1 h after feeding. |
|
Gene expression and the effect of knocking down genes associated with appetite regulation. (A) Analysis by qPCR of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA (bdnf) during paramecia feeding, n = 5, *P<0.05. (B and C) Western blots showing embryonic injection of neuropeptide Y (npy) MO (B) and preproinsulin a (insa) MO. (D) Embryonic injection of npy MO and npy mRNA. Orexigenic gene knockdown decreased feeding volume. (E) insa MO and insa mRNA, orexigenic gene knockdown increased feeding volume at 7 dpf. n = 15, *P<0.05. All values are mean ± SEM. (F and G) Knockdown of npy (F) and insa (G) affected locomotor activities at 5 dpf. n = 16, *P<0.05. All values are mean ± SEM. (H) Detection of gene knockdown for splicing MOs in 2% (w/v) agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
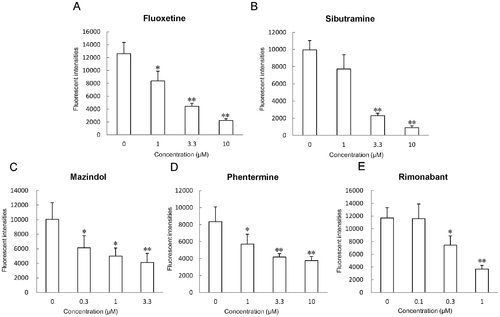
Effect of appetite suppressants on feeding volume. Effects of appetite-regulating drugs that are used clinically in humans affected zebrafish larvae. (A) Fluoxetine, (B) Sibutramine, (C) Mazindol, (D) Phentermine, and (E) Rimonabant treatment decreased feeding volume in young zebrafish (7 dpf). All values are mean ± SEM, n = 16, *P<0.05, **P<0.01. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
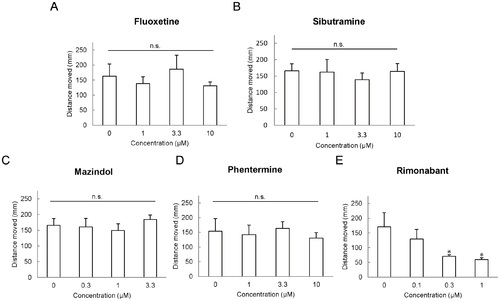
Effect of appetite suppressants on locomotor activities. The effects of appetite-regulating drug treatment on spontaneous swimming (15 min) were measured in young zebrafish. (A) Fluoxetine, (B) Sibutramine, (C) Mazindol, (D) Phentermine, and (E) Rimonabant. All values are mean ± SEM, n = 16, *P<0.01. PHENOTYPE:
|

Unillustrated author statements |