- Title
-
Zebrafish bcl2l is a survival factor in thyroid development
- Authors
- Porreca, I., De Felice, E., Fagman, H., Di Lauro, R., and Sordino, P.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
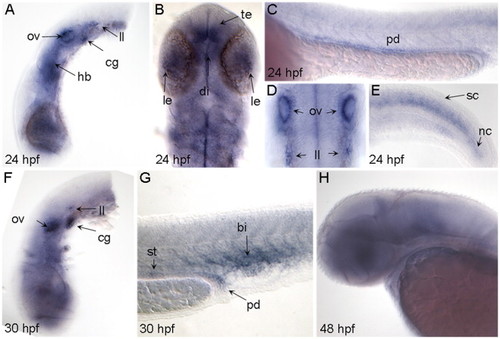
Expression of bcl2 during zebrafish development. Lateral views of embryos analyzed by ISH; anterior is to the left and dorsal to the top. (B) and (D) are dorsal views with anterior to the top. Stage is indicated at bottom left. (A)�(E) 24 hpf embryos showing expression in telencephalon (te), diencephalon (di), lens (le), hindbrain (hb), otic vesicles (ov), cranial ganglia (cg), lateral line primordium (ll), pronephric ducts (pd), spinal cord (sc) and notochord (nc). (F) and (G) 30 hpf embryos showing diffuse rostral expression with distinct domains in otic vesicles, cranial ganglia, distal segment of pronephric ducts, corpuscles of Stannius (st) and posterior blood island (bi). (H) 48 hpf embryo with diffuse bcl2 expression in the brain. |
|
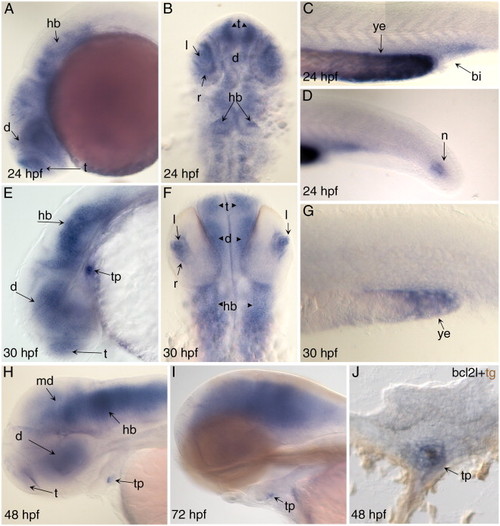
Expression ofbcl2lduring zebrafish development. Lateral views of embryos analyzed by ISH; anterior is to the left and dorsal to the top. (B) and (F) are dorsal view with anterior to the top. Stage is indicated at bottom left. (A)–(D) 24 hpf embryos showing expression in telencephalon (te), diencephalon (di), hindbrain (hb), lens (le), retina (re), posterior blood island (bi), yolk extension (ye) and notochord (no). (E)–(G) 30 hpf embryos showing expression in hindbrain, telencephalon, diencephalon, lens, retina, yolk extension and thyroid primordium (tp). (H) 48 hpf embryo showing expression in diencephalon, midbrain, hindbrain and thyroid primordium. (I) 72 hpf embryos showing expression in brain and thyroid primordium. (J) Cross section with double labeling of bcl2l mRNA (blue) and TG protein (brown) in a 48 hpf embryo showing expression of bcl2l in thyroid cells. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
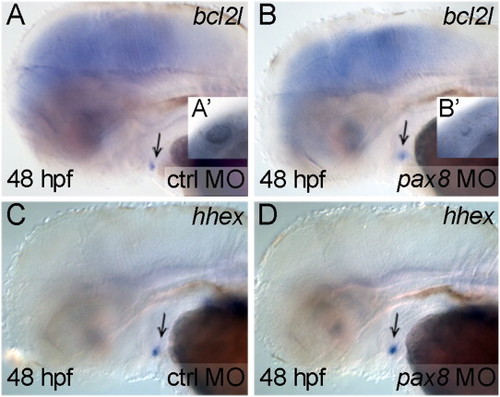
bcl2l expression in the zebrafish thyroid is not controlled bypax8. Lateral views with anterior to the left. Stage is indicated at bottom left, experimental morpholino at bottom right and marker at top right. (A) and (B) bcl2l expression in control (A) and in pax8 morphant embryos (B) is similar. (A′, B′) Morphology of the otic vesicles in control (A′) and pax8 morphant embryo (B′) at 24 hpf showing the efficiency of the injected MO (Mackereth et al., 2005). (C) and (D) hhex expression in the thyroid primordium of control (C) and pax8 morphant embryo (D) is similar. Arrow indicates the thyroid primordium. |
|
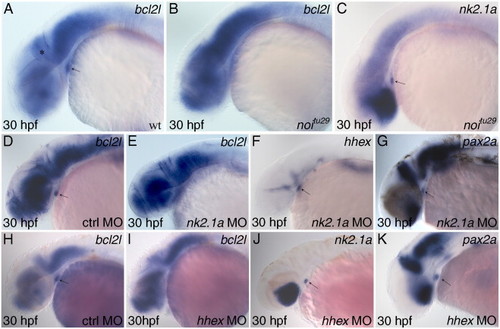
bcl2l expression in the thyroid is positively regulated bypax2a,nk2.1aandhhex. Lateral views with anterior to the left. Stage is indicated at bottom left, genotype or experimental morpholino at bottom right and marker at top right. (A) and (B) bcl2l expression in wild-type (A) and in noitu29 embryo (B) showing that bcl2l is not expressed in thyroid primordium when pax2a mRNA translation is inhibited. (C) nk2.1a expression in noitu29 embryo shows the presence of the thyroid primordium at this stage. (D) and (E) bcl2l expression in control (D) and nk2.1a morphant embryos (E) showing lack of bcl2l expression in the thyroid of a morphant embryo. Hhex (F) and pax2a (G) expression in nk2.1a morphant embryos shows the presence of the thyroid primordium at this stage. (H) and (I) bcl2l expression in control (H) and hhex morphant embryos (I) showing lack of bcl2l expression in the morphant embryo thyroid primordium. Nk2.1a (J) and pax2a (K) expression in hhex morphant embryos shows the presence of the thyroid primordium at the analyzed stage. Arrow indicates the thyroid primordium; asterisk the hindbrain–mindbrain boundary. |
|
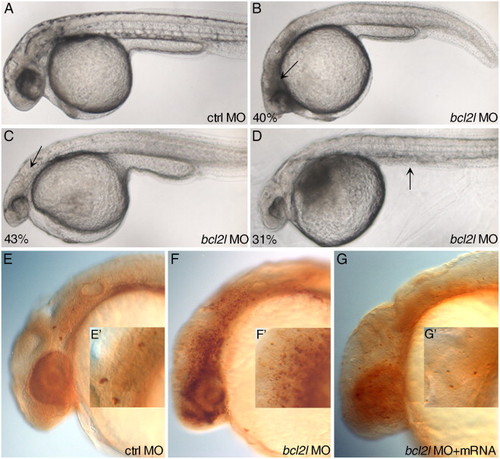
Morphology of bcl2l morphant embryos. Lateral views with anterior to the left of 24 hpf embryos. Experimental morpholino is indicated at bottom right, percentage (indicating the fraction of the described phenotype) at bottom left. (A) General morphology of control MO-injected embryo. (B)–(D) bcl2l MO injected embryos showing a broad region of opacity due to cell death in the head (arrow in (B)), hypoplastic central nervous system (arrow in (C)) and lack of yolk extension (arrow in (D)). (E)–(G) immunostaining at 24 hpf of active-caspase-3 in control MO (E), bcl2l MO (F) injected embryos and embryos co-injected with bcl2l MO and bcl2l mRNA (G). The strong activation of caspase-3 in bcl2l downregulated embryos is fully counteracted by co-injection of bcl2l mRNA. (E′), (F′), (G′) Magnifications of active caspase-3 positive cells in (E), (F) and (G). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
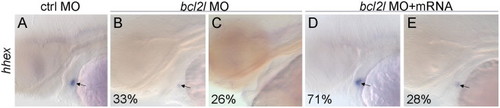
Alteration of thyroid development in bcl2l morphant embryos. Lateral views with anterior to the left of 48 hpf embryos. Experimental morpholino is indicated on the top and marker on the left of the figure, percentage (indicating the fraction of the described phenotype) at bottom left of each image. (A)–(E) hhex staining in control MO (A), bcl2l MO (B) and (C) injected embryos, and in bcl2l MO and mRNA co-injected embryos (D) and (E). Arrows point to the thyroid primordium. |
|
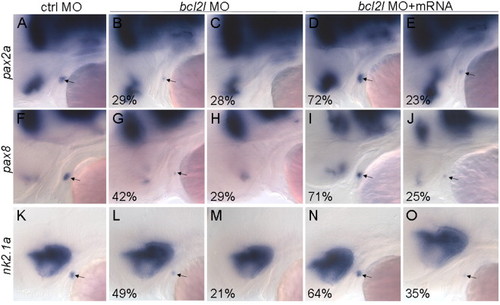
Thyroid development is severely impaired in bcl2l morphant embryos. Lateral views with anterior to the left of 48 hpf embryos. Experimental morpholino is indicated on the top and markers on the left of the figure, percentage (indicating the fraction of the described phenotype) at bottom left of each image. (A)–(E) pax2a staining in control MO (A), in bcl2l MO (B) and (C) injected embryos and in bcl2l MO and bcl2l mRNA co-injected embryos (D) and (E); (F)–(J) pax8 staining in control MO (F), in bcl2l MO (G) and (H) injected embryos and in bcl2l MO and bcl2l mRNA co-injected embryos (I) and (J); (K)–(O) nk2.1a staining in control MO (K), in bcl2l MO (L) and (M) injected embryos and in bcl2l MO and bcl2l mRNA co-injected embryos (N) and (O). Arrows point to thyroid primordium. |
|
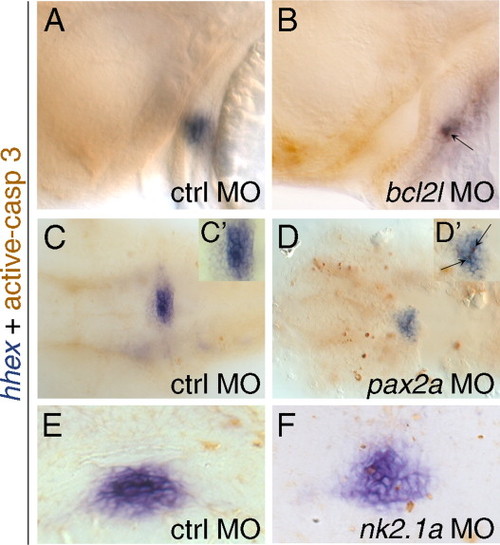
Activation of an apoptotic program in the thyroid primordium of bcl2l, pax2a or nk2.1a morphant embryos. Thyroid and apoptotic cells are stained with hhex riboprobe and active-caspase-3 antibody. Lateral (A) and (B) and ventral views (C) and (D) with anterior to the left, and cross sections (E) and (F) with anterior to the top, of 40 hpf embryos. Experimental morpholino is indicated bottom right, stage bottom left and markers on the left. (A) and (B) Embryos injected with control MO (A) or with bcl2l MO (B). (C) and (D) Embryos injected with control MO (C) or pax2a MO (D) deprived of yolk and flattened on their ventral side. (C′), (D′) Magnification of thyroid primordium in (C) and (D). (E) and (F) Embryos injected with control MO (E) or nk21a MO (F). Arrow indicates active-caspase-3 positive cells in the thyroid primordium. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
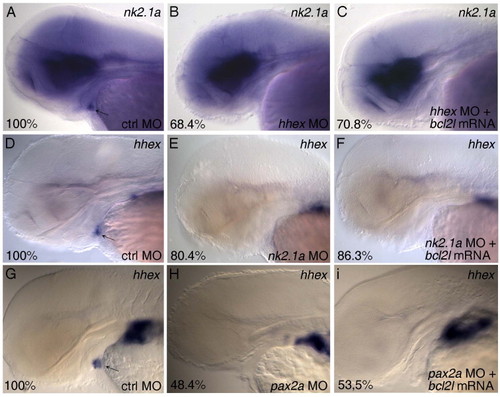
Bcl2l mRNA is not able to rescue the thyroid phenotype in nk2.1a, pax2a and hhex morphants. Lateral views with anterior to the left of 60 hpf embryos. Experimental morpholino and mRNA are indicated bottom right, markers top right and percentage (indicating the fraction of the described phenotype) bottom right of each panel. (A-C) nk2.1a staining in control MO (A), hhex MO (B) and hhex MO+bcl2l mRNA injected embryos (C); (D-F) hhex staining in control MO (D), nk2.1a MO (E) and nk2.1a MO+bcl2l mRNA injected embryos (F); (G-I) hhex staining in control MO (G), pax2a MO (H) and pax2a MO+bcl2l mRNA injected embryos (I). Arrows point to thyroid primordium. |
|
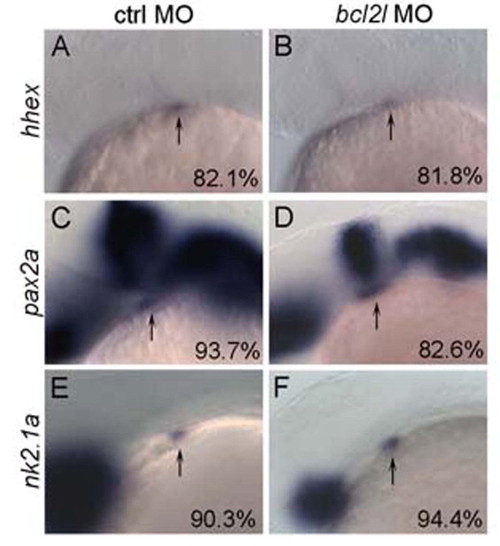
Early thyroid development is not impaired in bcl2l morphant embryos. Lateral views with anterior to the left of 28 hpf embryos. Experimental morpholino is indicated on the top and markers on the left of the figure, percentage (indicating the fraction of the described phenotype) at bottom right of each image. (A,B) hhex staining in control MO (A) and in bcl2l MO (B) injected embryos; (C,D) pax2a staining in control MO (C) and in bcl2l MO (D) injected embryos; (E,F) nk2.1a staining in control MO (E) and in bcl2l MO (F) injected embryos. Arrows point to thyroid primordium. |
|
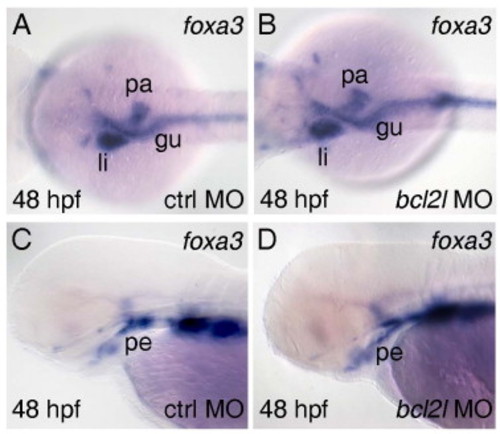
Endoderm derivatives are not affected by bcl2l dowregulation. (A, B) dorsal and (C, D) lateral views with anterior to the left of 48 hpf embryos. Experimental morpholino is indicated bottom right, stage bottom left and markers top right. (A, B) foxa3 staining in the trunk region of control MO (A) and bcl2l MO (B) injected embryos showing expression in liver (li), pancreas (pa) and gut (gu). (C, D) foxa3 staining in the head region of control MO (C) and bcl2l MO (D) injected embryos showing expression in pharyngeal endoderm (pe). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 366(2), Porreca, I., De Felice, E., Fagman, H., Di Lauro, R., and Sordino, P., Zebrafish bcl2l is a survival factor in thyroid development, 142-152, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.