- Title
-
Positive regulation of c-Myc by cohesin is direct, and evolutionarily conserved
- Authors
- Rhodes, J.M., Bentley, F.K., Print, C.G., Dorsett, D., Misulovin, Z., Dickinson, E.J., Crosier, K.E., Crosier, P.S., and Horsfield, J.A.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
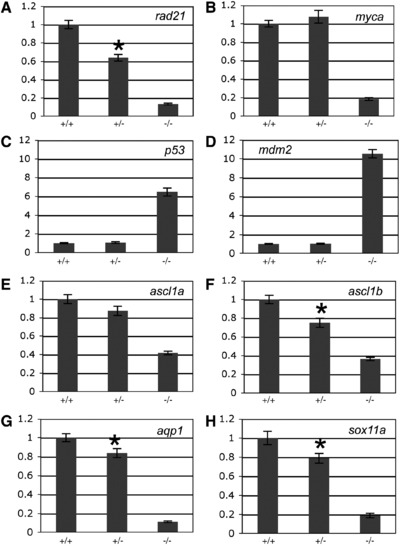
The effect of rad21 gene dose on the expression of genes regulated downstream of Rad21 in 48 h.p.f. embryos. A-H, quantitative PCR was used to measure the expression of rad21 (A), myca (B), p53 (C), mdm2 (D), ascl1a (E), ascl1b (F), aqp1 (G) and sox11a (H) from cDNA generated from pools of wild type (+/+), heterozygous rad21nz171 (+/-) and homozygous rad21nz171 (-/-) embryos. An asterisk indicates where the difference in expression between wild type and heterozygous rad21nz171 is statistically significant (p-value < 0.05). Values are relative to wild type and represent the mean ± s.e.m. of three cDNA samples each run in duplicate. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
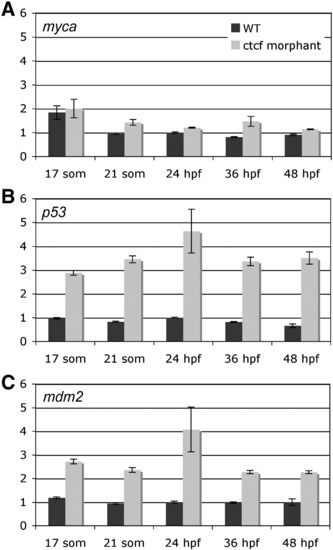
Expression of selected Rad21-responsive genes in ctcf morphants. A-C, quantitative PCR was used to measure the expression of myca (A), p53 (B) and mdm2 (C) in ctcf morphants relative to that in wild type embryos during early stages of embryonic development: 17 somites, 21 somites, 24 h.p.f., 36 h.p.f., 48 h.p.f.. Values are shown relative to wild type expression at 24 h.p.f., and are the mean ± s.e.m. of cDNA generated from pooled embryos run in duplicate. Data from three independent experiments are combined in Table 1, and graphs of one representative experiment for each gene are shown here. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Overlapping expression of rad21 and myca in wild type embryos. A–F, whole-mount wild type embryos stained for rad21 (blue) and myca (red-purple) expression at 24 h.p.f. (A–B), 48 h.p.f. (C–D) and 56 h.p.f. (E–F). Lateral views (panels A, C, E and F) and dorsal views (panels B and D) are shown of anterior regions. There is overlapping expression of rad21 and myca in cells of the ventricular zone (vz) at 24 h.p.f., and in tegmentum (te), midbrain–hindbrain boundary (mhb) and retinal ganglion cell layer (gcl) at 24 and 48 h.p.f. Only rad21 is expressed in the branchial arches (ba) at 56 h.p.f. |
|
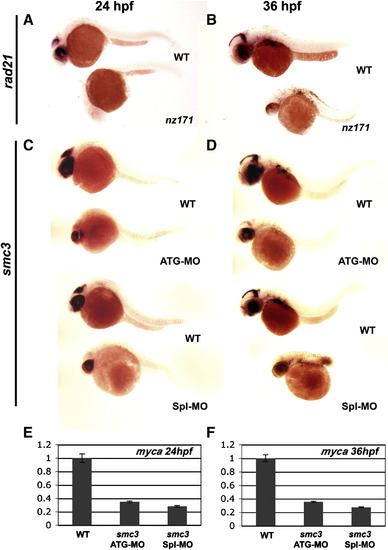
Reduced myca expression in rad21nz171 mutants and smc3 morphants. A, B, expression pattern of myca in whole-mount wild type and rad21nz171 embryos at 24 h.p.f. and 36 h.p.f. respectively (anterior to the left). myca expression (purple) in the brain and eye of wild type is absent in rad21nz171 embryos. C, D, Expression of myca is also greatly reduced in smc3 morphants at 24 h.p.f. and 36 h.p.f. respectively (anterior to the left). Embryos were injected with antisense morpholino oligonucleotides targeting the start codon (smc3ATG-MO) or the 3′ donor site of exon 1 (smc3Spl1-MO) of the smc3 gene to create two smc3 morphants. E, F, The expression of myca in smc3 morphants (smc3ATG-MO and smc3Spl-MO) is significantly reduced compared to wild type embryos as measured by quantitative PCR at 24 h.p.f. and 36 h.p.f. respectively. |
|
Targeting of zebrafish ctcf with antisense morpholino oligonucleotides. The ctcfSplx2-MO, 5′-CCAAAACAGATCACAAACCTGAAAG-3′ and the ctcfATG-MO, 5′-CATGGGTAATACCTACATTGGTTAA-3′ were designed using the ctcf sequence available at Ensembl (ENSDARG00000056621). The Splx2 morpholino targets the 3′ donor of exon 2, while the ATG morpholino targets the 5′ acceptor of exon 2 plus the ATG start codon. Both morpholinos should disrupt the splicing of both identified splice variants of ctcf. A, morphology of ctcfSplx2 morphants compared with wild type embryos at the indicated stages. 0.75 pmol of the ctcf morpholino was injected for each time point. Injection of the ctcfATG-MO at the higher dose of 1 pmol generated an identical phenotype (not shown). B, ctcf mRNA splicing is blocked by the ctcfSplx2-MO. cDNA was prepared from 24 h.p.f. zebrafish embryos. The electrophoretograms show RT-PCR products generated from cDNA. PCR primers used were Dr-CTCFsplx2-F 5′ATGATGATGGAAACCCTGGA 3′ (in exon 2) and Dr-CTCFsplx2-R1 5′ TCTTCATTTTGGGGTTCAGC 3′ (in exon 3); the larger 541 bp product in morphants corresponds to non-splicing of intron 2. Non-splicing is predicted to lead to a truncated protein. Left panel; intron 2 splicing of ctcf transcripts is abolished in surviving 24 h.p.f. embryos treated with 1 pmol Splx2-MO (uninjected embryos and genomic DNA used here as a reference). NB, this dose of MO elicits a 70% mortality rate with survivors severely disrupted/delayed. We therefore chose to use 0.75 pmol as an optimal dose (15% mortality, phenotype shown in A). Right panel; intron 2 splicing is significantly disrupted in embryos injected with 0.75 pmol ctcfSplx2-MO, compared with embryos treated with a control morpholino (control MO, Standard Negative Control Morpholino from GeneTools LLC). C, The ctcfATG-MO and ctcfSplx2-MO synergize to produce a more severe phenotype. (i), (ii), Each morpholino injected singly (0.5 pmol dose) generates a mild morphological phenotype (embryos on left) and modest changes in the transcription levels of aqp1 and mdm2 (graphs on right). (iii), In combination (0.5 pmol each), the two MOs elicit severe developmental delay (embryo on left) combined with dramatic downregulation of aqp1 and upregulation of mdm2 (graph on right). For (i)-(iii) myca expression is unchanged, regardless of MO identity or dose. Graphs represent gene expression of morphants (gray bars) relative to wild type (black bars). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
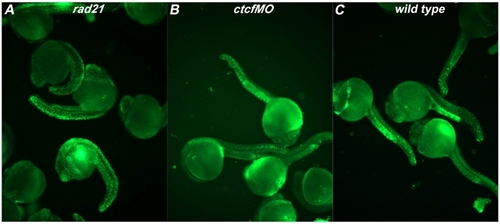
ctcf morphants do not exhibit increased apoptosis. Staining with acridine orange labels apoptotic cells and was performed on rad21nz171 mutants, ctcf morphants, and wild type controls at 24 h.p.f. ctcf morphants were obtained by injecting wild type embryos at the 1-4 cell stage with 0.75pM CTCF splx2 morpholino (ctcfMO: 5′CCAAAACAGATCACAAACCTGAAAG3′). Embryos were dechorionated and incubated in 5 μM acridine orange solution for 30 minutes. After rinsing in embryo medium, embryos were imaged with an Olympus IX71 microscope and DP Controller software. A. rad21nz171 mutants exhibit high levels of apoptosis as indicated by the presence of large numbers of acridine orange-positive cells. B, In contrast, ctcf morphants exhibit equivalent numbers of acridine orange-positive cells to the wild type embryos shown in C. Groups of 24 h.p.f. embryos are shown, and these are are representative of three independent experiments. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Validation of the zebrafish-specific Rad21 antibody. Protein lysates were prepared from 20 wild type (WT), sibling (sibs) and rad21nz171 homozygous mutant (mts) embryos at 27 h.p.f. A, Immunoblot showing Rad21 protein. B, α-tubulin loading control. Although there is less total protein in the mutant sample, the Rad21 protein is considerably more reduced in rad21nz171 mutants than can be expected due to loading discrepancy alone. As expected, siblings, comprising a mix of wild type and rad21nz171 heterozygotes, show intermediate levels of Rad21 protein. The band pattern detected, with the major band above 130kDa, is similar to that detected with commercial anti-human Rad21 antibodies. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 344(2), Rhodes, J.M., Bentley, F.K., Print, C.G., Dorsett, D., Misulovin, Z., Dickinson, E.J., Crosier, K.E., Crosier, P.S., and Horsfield, J.A., Positive regulation of c-Myc by cohesin is direct, and evolutionarily conserved, 637-649, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.