- Title
-
Blimp-1 is an essential component of the genetic program controlling development of the pectoral limb bud
- Authors
- Lee, B.C., and Roy, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
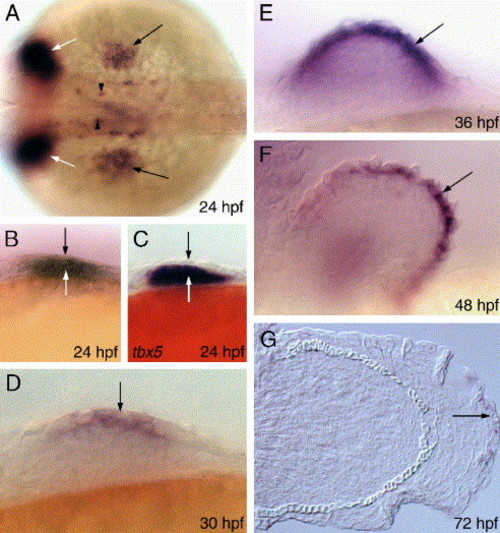
Spatio-temporal profile of blimp-1 expression in the developing pectoral fin. (A) A wild-type embryo, showing blimp-1 expression in the fin bud (black arrows). Expression in the pharyngeal endoderm (white arrows) and spinal cord neurons (arrowheads) is also indicated. (B) Expression at this stage is evident in the ectoderm (black arrow) and the mesenchyme (white arrow). (C) tbx5 expression shows localization only to the mesenchyme (white arrow) and is excluded from the ectoderm (black arrow). (D) blimp-1 expression in the mesenchyme decreases and strengthens in the ectoderm (arrow). (E-G) blimp-1 expression in succeeding stages of embryogenesis. Panel A depicts dorsal view, all others depict lateral views. All panels of this and subsequent figures are oriented anterior to the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
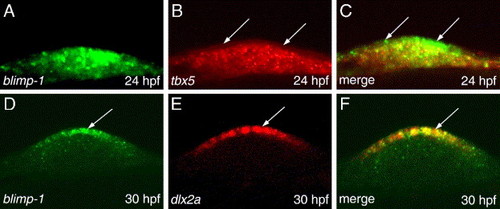
Comparative analysis of the mesenchymal and ectodermal components of blimp-1 expression with respect to tbx5 and dlx2a using double label fluorescent in situ hybridization. (A) A wild-type embryo, showing blimp-1 expression in the fin bud. (B) The same embryo showing tbx5 expression in the fin bud. The ectoderm, which is devoid of tbx5 transcripts, is indicated (arrows). (C) Superimposition of the images depicted in panels A and B, showing colocalization of blimp-1 and tbx5 signals in the mesenchyme, while ectodermal cells only contain blimp-1 transcripts (arrows). (D-F) blimp-1 and dlx2a are co-expressed in cells of the AER from 30 hpf (arrow). All panels depict lateral views. |
|
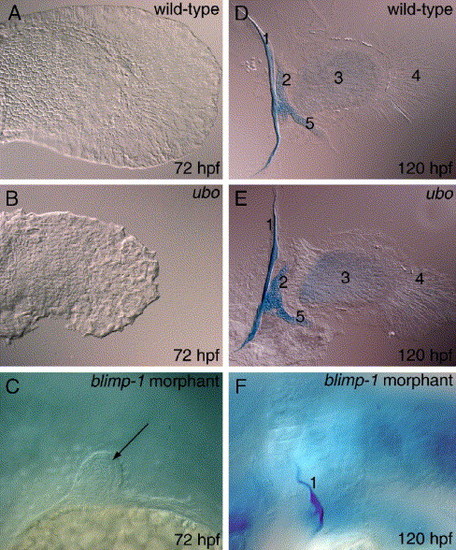
Pectoral fin development is affected in embryos compromised in Blimp-1 activity. (A) Normarski image of a wild-type fin. (B) Fin of a homozygous ubo mutant embryo. (C) Rudimentary fin bud of a blimp-1 morphant embryo. (D-F) Alcian blue stain of the pectoral fin skeletal elements of a wild-type, ubo mutant and blimp-1 morphant embryo. 1 = cleithrum, 2 = scapulocoracoid, 3 = endoskeletal disk, 4 = actinotrichs, 5 = postcoracoid process. All panels show lateral views. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
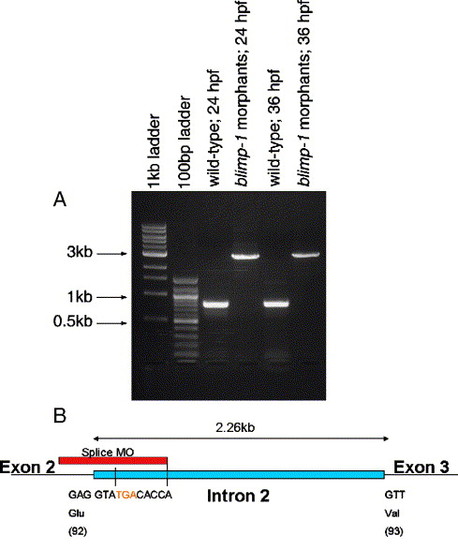
Splice junction targeted anti-blimp-1 MOs effectively block splicing of blimp-1 pre-mRNA. (A) RT-PCR of mRNA extracted from wild-type embryos and blimp-1 morphants, showing the expected 783 bp band in the wild-type lanes and an approximately 3 kb band in those of the morphants. The primer pair used for the PCR reaction amplifies across exons 1-5 (see Materials and methods). (B) Diagram illustrating the target site of the MO, at the junction between exon 2 and intron 2. The last codon of exon 2 and the first codon of exon 3, together with their corresponding amino acid, are indicated. The premature stop codon in the mis-spliced blimp-1 mRNA is highlighted in red. |
|
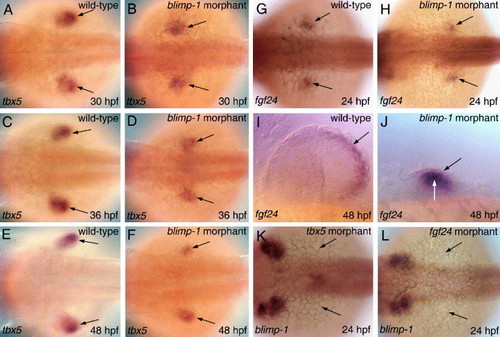
blimp-1 acts downstream of tbx5 and fgf24. (A-F) tbx5 expression in the fin buds (arrows) of wild-type and blimp-1 morphants. (G and H) fgf24 expression (arrows) in a wild-type embryo and a blimp-1 morphant. (I) A wild-type fin, showing fgf24 expression in the AER (arrow). (J) A blimp-1 morphant at the same stage, showing absence of fgf24 from the ectoderm (black arrow) and its continued expression in the mesenchyme (white arrow). (K and L) blimp-1 expression is absent (arrows) from the prospective fin buds of tbx5 and fgf24 MO injected embryos. All panels depict dorsal views, except panels I and J, which depict lateral views. |
|
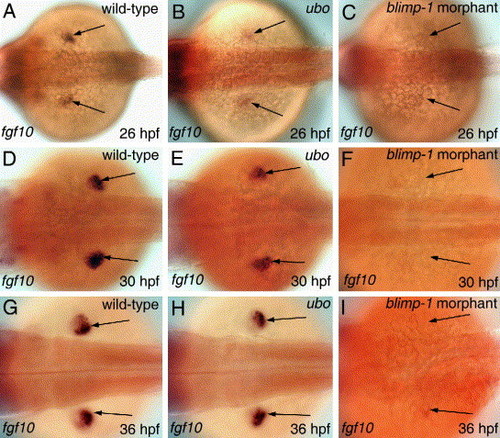
Blimp-1 activity is required for fgf10 expression in the fin bud mesenchyme. (A-I) fgf10 expression in the fin mesenchyme (arrows) of wild-type, ubo and blimp-1 morphant embryos at specific developmental stages. All panels depict dorsal views. |
|
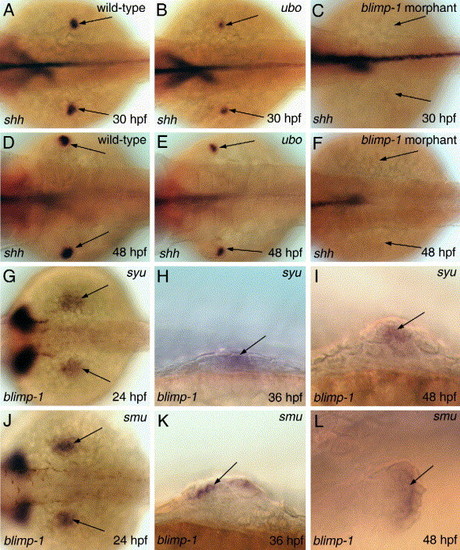
Blimp-1 function is necessary for shh expression whereas Hh signaling is required for maintenance, but not the initiation, of blimp-1 expression. (A-F) shh expression (arrows) in the ZPA of wild-type, ubo mutant and a blimp-1 morphant embryos at specific developmental stages. (G-I) blimp-1 expression (arrows) in embryos lacking Shh activity. (J-L) blimp-1 expression (arrows) in embryos lacking Smo activity. Panels A-F, G and J depict dorsal views; panels H, I, K and L show lateral views. |
|
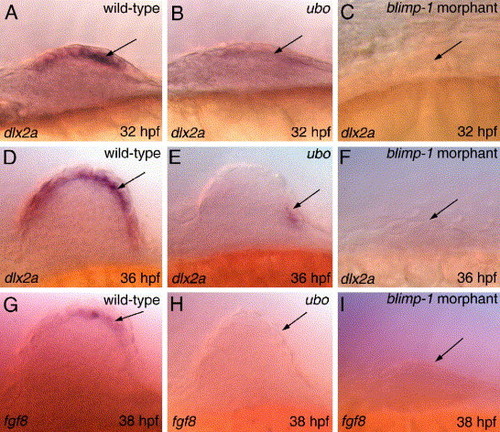
Blimp-1 activity is crucial for the establishment the AER. (A-F) dlx2a expression in the AER (arrow) of a wild-type, ubo mutant and a blimp-1 morphant embryo. (G-I) fgf8 expression in the AER (arrow) of a wild-type, ubo mutant and a blimp-1 morphant embryo. All panels depict lateral views of developing pectoral fin buds. |

Unillustrated author statements |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 300(2), Lee, B.C., and Roy, S., Blimp-1 is an essential component of the genetic program controlling development of the pectoral limb bud, 623-634, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.