- Title
-
Cloning, expression, and alternative splicing of neogenin1 in zebrafish
- Authors
- Shen, H., Illges, H., Reuter, A., and Stürmer, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Mech. Dev.
|
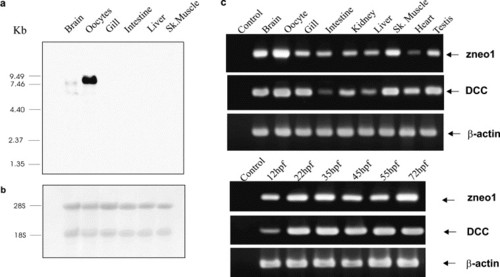
Expression of neogenin and DCC mRNAs in zebrafish. (a) Northern analysis of zneo1 transcripts in zebrafish tissues. Total RNA, 20 µg, from various tissues were fractionated on 1% denaturing agarose-formaldehyde gel and hybridized with a 1 kb 32P-labeled zneo1 probe according to standard protocols. Two zneo1 transcripts of 6.5 and 7.5 kb were detected only in brain and oocytes. The relative mobility of molecular weight marker is indicated on the left in kb. (b) Methylene blue staining of 18 and 28 s rRNAs revealed the integrity and comparable amount of total RNA used in (a). (c) Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis for zneo1 and DCC mRNA expression in adult and embryonic zebrafish. RT-PCRs were performed with gene-specific primers. No-RT (data not shown) and no-template controls were involved in all the reactions giving no non-specific product. β-actin RT-PCR was used to standardize the reactions. hpf, hours post-fertilization. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
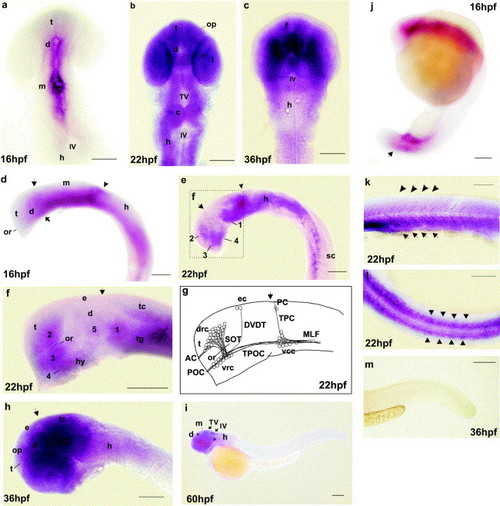
Expression of zneo1 transcripts in the zebrafish embryo. Whole-mount in-situ hybridization was performed with a 600 bp digoxygenin-labeled cRNA probe for zneo1 as described by Thisse et al., 1993. (a-c), dorsal view, while rostral is up. (d-i, k, m), lateral view, rostral to the left. (l), dorsal view, rostral to the left. (j), lateral view, and dorsal is up. (a), (d), and (j), 16 hpf. Zneo1 expression is evident in the ventricular zone of forebrain and midbrain (a), and tail region (arrow in (j)), weak in hindbrain (d), and not detected in the telencephalon (a and d). Arrow, forebrain-midbrain boundary; arrowhead, midbrain-hindbrain boundary; solid arrow, location of ventrocaudal cluster of the first neurons. (b) 22 hpf. Staining is seen along the rostrocaudal axis in most regions of the brain, olfactory placode (op), lens primordium (l), and the still undifferentiated retina (r). (e) and (f), 22 hpf. In the forebrain and midbrain, zneo1 is expressed by five clusters of cells, that is, 1, in the ventral tegmentum extending caudally toward the hindbrain and dorsally toward the rostral tectum (tc); 2, in the telencephalon dorsal to the optic recess (or); 3, ventral to or, in the rostral diencephalon; 4, ventral to 3, extending caudally into the hypothalamus (hy); 5, central domain of diencephalon. (f) is a higher magnification of the box marked in (e). The arrow denotes an expression gap closer to the forebrain-midbrain boundary. Arrowhead, midbrain-hindbrain boundary. (g) 22 hpf. Schematic illustration of the first neuronal clusters and their axonal processes in approximate 22 hpf embryo, according to Chitnis and Kuwada (1990) for comparison. Four neuronal clusters are present in the forebrain and midbrain: drc, the dorsorostral cluster; vcc, the ventrocaudal cluster; vrc, the ventrorostral cluster; and ec, the epiphyseal cluster. The drc projects axons pioneering the supraoptic tract (SOT) and anterior commissure (AC); vrc grows axons contributing to the tract of the postoptic commissure (TPOC) and postoptic commissure (POC); vcc extends axons that form the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF), the tract of the posterior commissure (TPC), and the posterior commissure (PC); and ec grow axons that contribute to the dorsoventral diencephalic tract (DVDT). Arrow indicates the forebrain-midbrain boundary. (c) and (h), 36 hpf. Staining is intensified in the midbrain but is decreased in hindbrain. Arrow, forebrain-midbrain boundary. (i) 60 hpf. Expression is decreased to the tectal and the fourth VZs, (TV and IV), a longitudinal strip ventral to midbrain and hindbrain (bracketed) and diencephalon. (k) and (l), 22 hpf. Transient zneo1 expression is stronger in the ventral part of the somites (arrows) than the dorsal part (arrowheads). (m), 36 hpf. Staining in the somites is no more detectable. c, cerebellum; d, diencephalon; e, epiphysis; f, forebrain; h, hindbrain; hpf, hours post-fertilization; hy, hypothalamus; IV, the fourth ventricle; l, lens; m, midbrain; op, olfactory placode; or, optic recess; r, retina; sc, spinal cord; t, telencephalon; tc, tectum, tg, tegmentum; TV, tectal ventricle. Scale bar, is 50 µm in (a), (d) and (j), 200 µm in (i), and 100 µm in all others. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Expression of zneo1 splice variants in zebrafish. (a) Schematic representation of RT-PCRs used for alternative splicing study. RT-PCR was performed with the indicated primers: znsp1, TCACGCACAGACCATCAAAG; znsp1′, TGGTCTTCCAACGCACTGTA; znsp2, CTGTAGTGAGCAAAGAGG; znsp2′, AGGTCTGGTGGTTTGAGA; znsp3, GGGCAACTCCAAAGATCTCAA; znsp3′, TGAAAGGTCAGTGGTGCAAGA under standard conditions. The resulting products derived from the first strand cDNAs of various adult tissues and staged embryos were subsequently cloned and sequenced. The possible splice isoforms are illustrated in the figure and named after the region amplified and the presence or absence of the alternative splices. FN4-FN6, fibronectin type III domains 4-6; hpf, hours post-fertilization; sp1-sp4, alternative splice 1-4 (indicated by dotted lines); TM, transmembrane domain. (b) Expression of zneo1 splice variants in adult and embryonic zebrafish. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 118(1-2), Shen, H., Illges, H., Reuter, A., and Stürmer, C., Cloning, expression, and alternative splicing of neogenin1 in zebrafish, 219-223, Copyright (2002) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.