- Title
-
dino and mercedes, two genes regulating dorsal development in the zebrafish embryo
- Authors
- Hammerschmidt, M., Pelegri, F., Mullins, M.C., Kane, D.A., van Eeden, F.J., Granato, M., Brand, M., Furutani-Seiki, M., Haffter, P., Heisenberg, C.P., Jiang, Y.J., Kelsh, R.N., Odenthal, J., Warga, R.M., and Nüsslein-Volhard, C.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
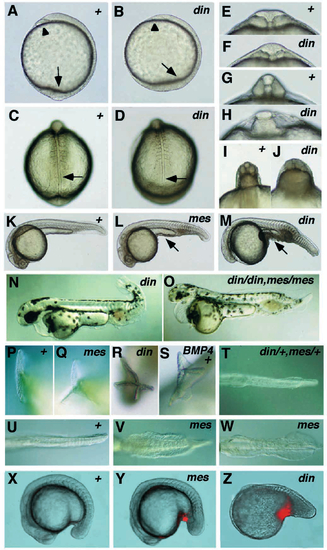
Morphological characteristics of the dino (dintm84) and mercedes (mestm305) mutant embryos. Wild-type embryos are indicated with ‘+’. (A,B) Tailbud stage, lateral view: the pillow is marked with an arrowhead, the tailbud with an arrow. (C,D) 8-somite stage, dorsal view: the end of the notochord and the corresponding position in the wild-type embryo are marked by an arrow. (E,F) 3- somite stage, optical cross section at the level of the 2nd somite: the anterior somites of the mutant are smaller and the neural tube is of normal size. (G,H) 8-somite stage, optical cross section at the level of the 6th somite: the notochord is lost and the somites are fused in dino mutants with a strong phenotype. (I,J) 15-somite stage, optical cross section at the level of the 13th somite: the posterior somites are larger and the neural tube is smaller in dino mutants. (K,L,M) 24 hours, lateral view: cells at the ventral side of the yolk extension are marked with an arrow. (N,O) 48 hours, lateral view: note the smaller head in the din mes double mutant. (P-S) 36 hours, posterior view of tail fin; (S) wild-type embryo injected with Xenopus Bmp-4 mRNA. (T-W) 36 hours, ventral view of tail fin: (V) mestm305/mestm305 embryo from heterozygous mother; (W) mestm305/mestm305 embryo from homozygous mother. (X-Z) Lateral views of (X) wild-type, 20- somite stage embryo; (Y) mestm305, 20-somite stage embryo; (Z) dintt250, 15-somite stage embryo, showing acridine orange staining. Apoptotic cells (red) can be detected ventral of the forming yolk extension in din and mes mutant embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
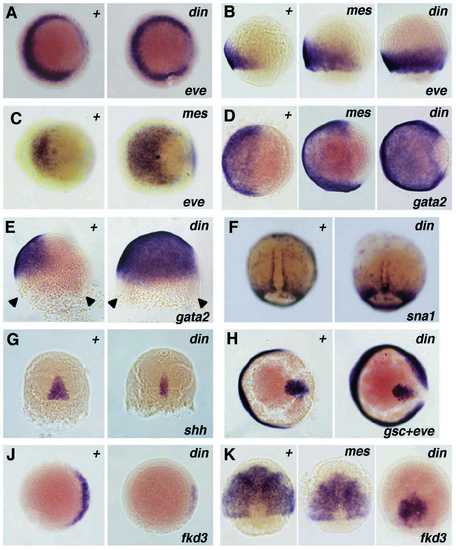
Altered gene expression in dino (dintm84) and mercedes (mestm305) mutants during gastrulation, detected by whole- mount in situ hybridization. Expression of: (A) eve1, at 40% epiboly, animal view, dorsal right; (B) eve1, at 70% epiboly, lateral view, dorsal right; (C) eve1, at tailbud stage, vegetal view, dorsal right – the more pronounced staining reflects the expression of eve1 in a group of cells posterior to the Kupfer’s vesicle (Joly et al., 1993); (D) gata2, at 70% epiboly, animal view, dorsal right; (E) gata2, at 70% epiboly, lateral view, dorsal right – the margin of the blastoderm is indicated by arrowheads; (F) sna1, at 80% epiboly, dorsal view; (G) shh, at 70% epiboly, dorsal view; (H) gsc and eve1, at 70% epiboly, animal view, dorsal right; (J) fkd3, at shield stage, animal view, dorsal right. (K) fkd3, at 70% epiboly, dorsal view. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
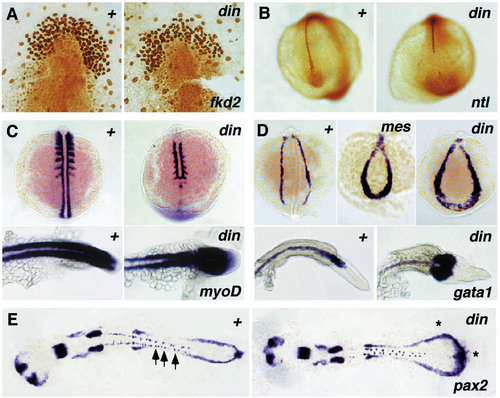
Altered gene expression in mesodermal tissues of dino (dintm84) and mercedes (mestm305) mutants detected by in situ hybridization (C-E) and immunostaining (A,B). (A) fkd2, 10-somite stage, dorsal view of the head region. (B) ntl, 10-somite stage, dorsal view. (C) myoD: top, 10-somite stage, dorsal view; bottom, 22 hours, ventral view of the tail. (D) gata1: top, 10-somite stage, dorsal view; bottom, 22 hours ventral view of the tail. (E) pax2, 22-somite stage, dorsal view of a spread embryo, anterior to the left. The pronephric expression domain is indicated by asterisks (in the mutant), the interneurons are indicated by arrows (in the wild type). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|