- Title
-
Bringing tendon biology to heel: Leveraging mechanisms of tendon development, healing, and regeneration to advance therapeutic strategies
- Authors
- Tsai, S.L., Nödl, M.T., Galloway, J.L.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
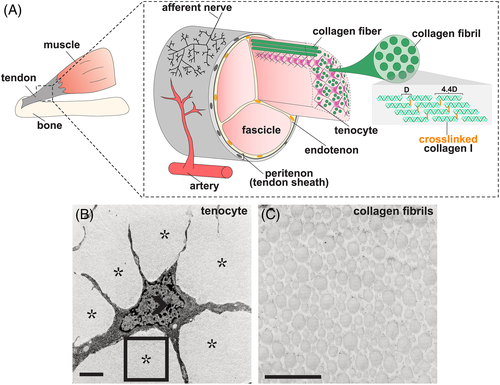
Tendon structure. A, Graphical representation of tendon morphology. The tendon midsubstance is comprised of collagen molecules which are spaced apart at a distance of 67 nm (letter D in diagram) and cross‐linked to form stable fibrils.15 Tenocytes are interspersed between collagen fibrils, which together generally form higher order bundles called fascicles. Fascicles are held together by connective tissue called the endotenon. The tendon midsubstance is encased in the peritenon, or tendon sheath, which is comprised of a basement membrane and epithelial cell layer.16 B,C, Transmission electron micrograph (TEM) of 6‐week‐old mouse tenocyte, B, and collagen fibrils, C. Open arrowhead marks cell nuclei and asterisks mark collagen fibrils. Rectangle in, B, is shown at higher magnification in, C. Scale bar, 1 μm. Images in, B,C, were adapted from Kalson et al17 |
|
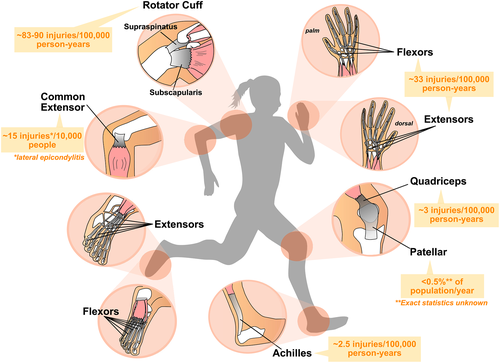
Major force‐bearing limb tendons in the human body. Diagram depicting the structure of major limb tendons that are frequently injured including the digital flexor and extensor tendons, common extensor, Achilles, rotator cuff, and patellar tendons. Muscles are depicted in pink, tendons in grey, and bone in white. Average incidence of injuries among the general population (predominantly US statistics) is shown in orange.67-72 Rates of tendon rupture or disease vary with age and population demographics of geographical location or study |
|
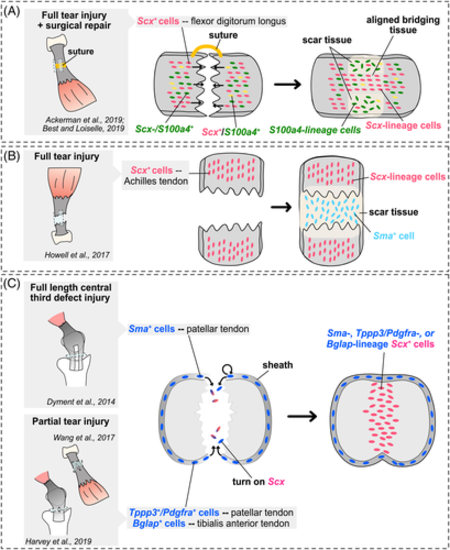
Summary of lineage tracing studies in mouse tendon healing models. A‐C, Schematics illustrating main conclusions of mouse tendon healing genetic lineage tracing studies in various tendon midsubstance injury models and limb tendons. Studies assessing contribution of cells from the midsubstance are shown inA and B, while studies assessing contribution of cells from the tendon sheath are shown in C. Sagittal views are shown in the cartoons in A and B, while a transverse view is shown in C |