FIGURE SUMMARY
- Title
-
Evolution of caudal fin ray development and caudal fin hypural diastema complex in spotted gar, teleosts, and other neopterygian fishes
- Authors
- Desvignes, T., Carey, A., Postlethwait, J.H.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
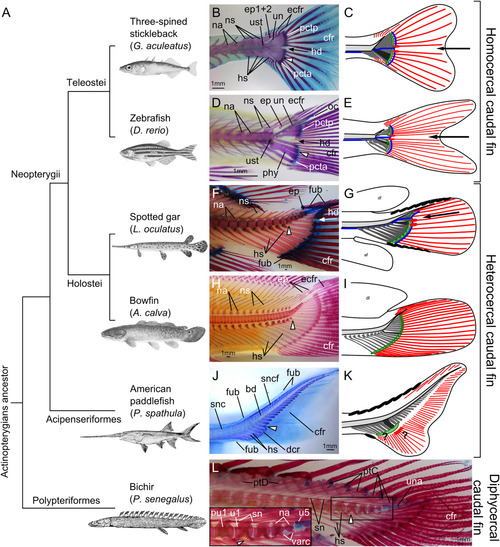
Evolution of the caudal fin skeleton in actinopterygians. A: Phylogenetic relationships of actinopterygians investigated here (after Near et al., 2012, 2014; Betancur‐R et al., 2013, 2017). B,D,F,J,L: Alcian Blue and Alizarin Red cleared and stained skeletons. H: Alizarin Red cleared and stained skeleton. B,C: Adult three‐spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus), 69 mm TL. D,E: Adult zebrafish (Danio rerio), 28 mm TL. F,G: Adult spotted gar (Lepisosteus oculatus), 493 mm TL. H,I: Adult bowfin (Amia calva) 233 mm TL. J,K: Young American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula), 84 mm TL. L: Adult bichir (Polypterus senegalus), 161 mm TL. For each species, the white elongated triangle indicates hypural 1 as a reference. In B‐G, the arrow points to the hypural diastema. Scale bars = 1 mm. bd, basidorsal arcualia; cfr, caudal fin rays; dcr, distal caudal radials; ecfr, epichordal caudal fin rays; ep, epurals; ep1+2, compound epural made by the fusion of epurals 1 and 2; fub, basal fulcra; hd, hypural diastema; hs, haemal spines; oc, opisthural cartilage; na, neural arches; ns, neural spine; phy, parhypural; pcta, anterior plate of connective tissue; pctp, posterior plate of connective tissue; ptC, pterygiophores of the caudal fin; ptD, pterygiophores of the dorsal fin; pu1, preural centrum 1; sn, supraneurals; snc, supraneurals of the caudal skeleton; sncf, supraneurals of the caudal fin skeleton; un, uroneural; una, ural neural arch; ust, urostyle; u1, ural centrum 1; u5, ural centrum 5; varc, ventral arcualia. In the schematic representations of caudal fin organization (C,E,G,I,K), the notochord is represented in light gray, the haemal elements in dark gray, and the first hypural in black. Plate(s) of connective tissue are represented in green. A black arrow points at the hypural diastema in teleosts (C,E) and gar (G). Caudal vasculature is represented in blue in teleosts (C,E) and gar (G) based on literature and previously published information (Schultze and Arratia, 1986, 1988; Arratia and Schultze, 1992; Arratia, 2013, 2015; Wiley et al., 2015; Desvignes et al., 2018) as well as histological observations in zebrafish and gar (cf. Fig. 3); the vasculature is not shown for bowfin (I) and paddlefish (K) because it is unknown or inconsistently positioned. Caudal lepidotrichia are represented in red, with the earliest‐forming lepidotrichia marked with an oval at their base. Fulcra are represented with plain black ovals on the dorsal and/or ventral leading edge of the fin in gar (G) and paddlefish (K). Question marks in paddlefish (K) denote uncertainty concerning the plate of connective tissue and the earliest‐forming caudal lepidotrichia. Abbreviations: af, anal fin; df, dorsal fin.
|
|
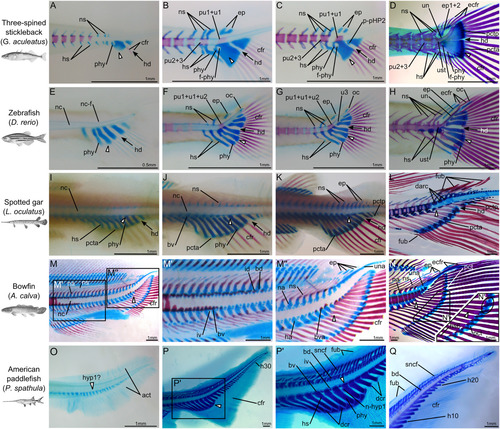
Developmental details of the caudal fin skeleton in stickleback, zebrafish, spotted gar, bowfin, and American paddlefish. A‐D: Three‐spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus), 6.5 mm TL (A), 7 mm TL (B), 7.5 mm TL (C) and 15 mm TL (D). E‐H: Zebrafish (Danio rerio) 4.5 mm TL (E), 5 mm TL (F), 5.5 mm TL (G), and 6 mm TL (H). I‐L: Spotted gar (Lepisosteus oculatus), 17 mm TL (I), 19 mm TL (J), 26 mm TL (K), and 85 mm TL (L). M,N: Bowfin (Amia calva), 34 mm TL (M‐M″) and 99 mm TL (N). O‐Q: American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula), 12 mm TL (O), 65 mm TL (P‐P′) and 85 mm TL (Q). L: Detail of the posterior part of the notochord of Fig. 1J. For each species, the white elongated triangle indicates hypural 1 as a reference. In A‐L the black arrow points at the hypural diastema. In the insert in N, the oval circles the distal ends of hypurals 2 and 3 showing an unbroken plate of connective tissue. act, actinotrichia; bd, basidorsal arcualia; bv, basiventral arcualia; bva, basiventral autocentra; cfr, caudal fin rays; darc, dorsal arcualia; dcr, distal caudal radials; ecfr, epichordal caudal fin rays; ep, epurals; ep1+2, compound epural made by the fusion of epurals 1 and 2; f‐phy, foramen created by the parhypural; fub, basal fulcra; ha, haemal arches; hd, hypural diastema; hs, haemal spines; hyp1?, putative hypural 1; h10, hypural 10; h20, hypural 20; h30, hypural 30; id, interdorsal arcualia; iv, interventral arcualia; oc, opisthural cartilage; n‐hyp1, notch at the base of hypural 1; na, neural arches; nc, notochord; nc‐f, notochord point of flexion; ns, neural spine; phy, parhypural; pct, plate of connective tissue; pcta, anterior plate of connective tissue; pctp, posterior plate of connective tissue; p‐pHP2, anterior process of the posterior hypural plate; pu1+u1, compound centrum made by the fusion of preural centrum 1 and ural centrum 1; pu2+3, compound centrum made by the fusion of preural centra 2 and 3; pu1+u1+u2, compound centrum made by the fusion of preural centrum 1 and ural centra 1 and 2; sncf, supraneurals of the caudal fin skeleton; un, uroneural; una, ural neural arch; ust, urostyle; u3, ural centrum 3.
|
|
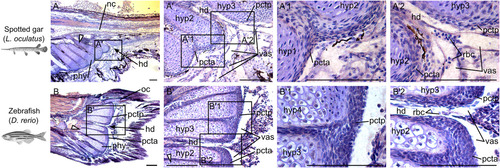
Orcein stains for elastin in plates of connective tissue in spotted gar and zebrafish. Sagittal sections of caudal fin regions of (A) a 24 mm TL spotted gar larva (∼22 dpf) and (B) a 13 mm TL zebrafish (21 dpf) stained with Orcein (red‐rusty color) and counter stained with Gills hematoxylin (blue‐purple). Scale bar = 100 μm. White elongated triangles indicate hypural 1 and black arrows point at the hypural diastema. hd, hypural diastema; hyp, hypural; nc, notochord; oc, opisthural cartilage; pcta, anterior plate of connective tissue; pctp, posterior plate of connective tissue; phy, parhypural; rbc, red blood cells; vas, vasculature.
|
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Dev. Dyn.