- Title
-
Semaphorin 5A is a bifunctional axon guidance cue for axial motoneurons in vivo
- Authors
- Hilario, J., Rodino-Klapac, L.R., Wang, C., and Beattie, C.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
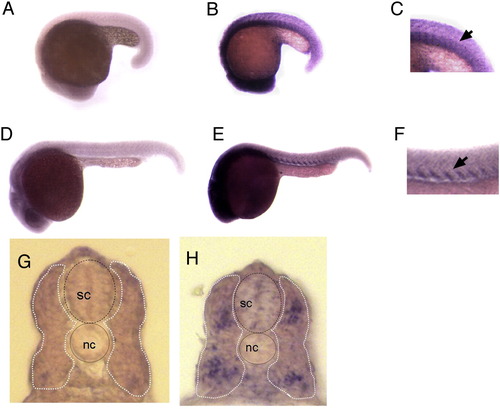
sema5A is expressed in the myotome at 18 and 24 hpf. RNA in situ hybridization shows expression of sema5A. (A, D, G) Sense and (B, E, H) anti-sense riboprobes were used. (C, F) Higher magnification views of trunk region of panels B and E. (G, H) 20 µm cross-sections of in situ labeled 24 hpf embryos. Spinal cord (sc) and notochord (nc) are indicated. The myotome is outlined by dashed white line. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
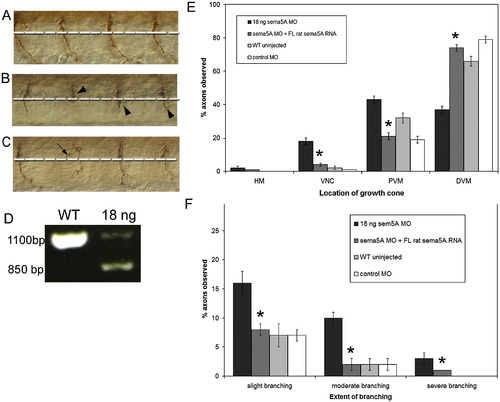
Morpholino knockdown of zebrafish Sema5A results in delay in CaP axon extension and axonal branching and is rescued by full-length rat Sema5A mRNA. (A–C) Lateral views of whole mount antibody labeling with znp1 of sema5A MO injected 26 hpf embryo (B, C) and uninjected WT sibling (A). Dashed white line indicate first intermediate target. Arrowheads indicate delayed axons. Arrow indicate an aberrant branch (D) RT-PCR showing efficacy of sema5A splice site MO in inducing aberrant splicing of sema5A mRNA in MO-injected embryos compared to uninjected wild type embryos. (E) Axon position was scored using different landmarks along the axon pathway in a dorsal to ventral direction. The landmarks on the x-axis are the horizontal myoseptum (HM), ventral edge of the notochord (VNC), proximal portion of the ventral muscle (PVM) and distal portion of the ventral muscle (DVM). (F) The axonal branching phenotype was scored by classifying branched axons into slight, moderate or severe branching. Data were quantified in sema5A MO injected embryos (n = 2020 axons, 101 embryos), sema5A MO and rat full-length sema5A RNA co-injected embryos (n = 2580, 129 embryos), WT uninjected (n = 1640 axons, 89 embryos) and control MO injected embryos (n = 2360 axons, 118 embryos) with embryos obtained from at least three separate experiments. Error bars represent confidence interval for proportions at 95% confidence. Asterisks indicate significant difference between 18 ng sema5A MO-injected embryos and sema5a MO + rat sema5a RNA injected embryos at p < 0.001 using one-way ANOVA. |
|
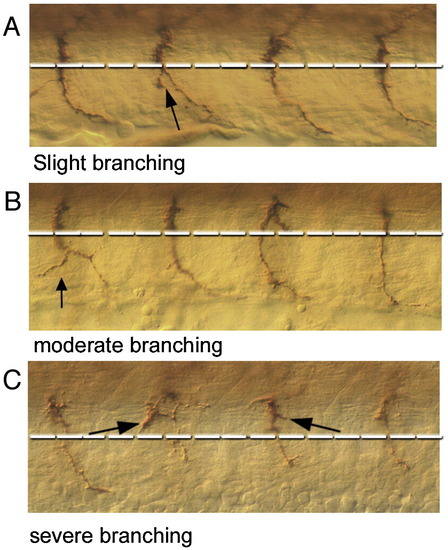
CaP axon branching. Examples of different extents of branching observed in embryos (A) arrowhead indicates an axon with a slight branch characterized by short, thin extensions from the main axon trunk. (B) Arrowhead indicates axon displaying moderate branching characterized by either a longer extension from the main axon path into the surrounding myotome or a slightly thicker extension (C) arrowhead indicates a severely branched axon which is characterized by numerous and disordered branches. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
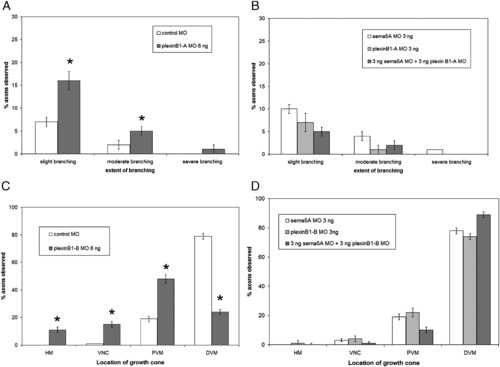
plexin B1-A and plexin B1-B morpholino injection phenotypes and co-injections with sema5A. (A) Injection of 6 ng plexin B1-A MO shows an increase in branching CaP axons compared to control MO injected embryos. (B) Co-injection of 3 ng plexin B1-A MO and sema5A MO has little or no difference with injection of each MO by itself at 3 ng. (C) Injection 6 ng plexin B1-B MO results in a delay in CaP axon extension into the ventral myotome compared control MO injected embryos. (D) Co-injection of 3 ng of plexin B1-B MO and sema5A MO displayed no delay of CaP axon extension phenotype. Data quantified from 3 ng sema5A MO injected embryos (n = 2020 axons, 101 embryos), 6 ng plexin B1-A MO injected embryos (n = 1040 axons, 52 embryos), 3 ng plexin B1-A MO injected embryos (n = 940 axons, 47 embryos), 3 ng sema5A MO + 3 ng plexin B1-A MO injected embryos (n = 2140 axons, 107 embryos), 6 ng plxnB1B MO injected embryos (n = 1960 axons, 98 embryos), 3 ng plexin B1-B MO injected embryos (n = 1080 axons, 54 embryos), 3 ng sema5A MO + 3 ng plexin B1-B MO injected embryos (n = 1180 axons, 59 embryos). Error bars represent confidence interval for proportions at 95% confidence. Asterisks indicate significant difference between control MO injected and plexin B1-A or plexin B1-B MO injected with p < 0.001 using one-way ANOVA. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
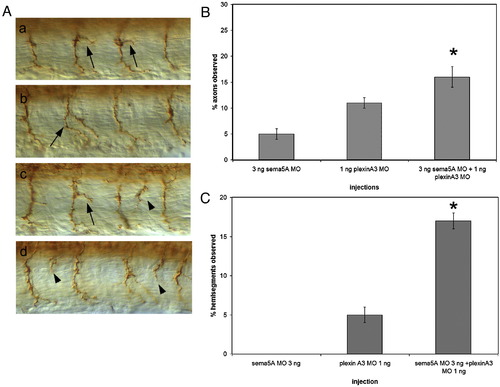
Additive and synergistic interactions of Sema5A and Plexin A3. (A) Axonal phenotypes observed in embryos injected with plexin A3 MO alone or plexin A3 MO and sema5A MO. Arrows indicate moderately and severely branched CaP axons, arrowheads indicate axons exiting the spinal cord at ectopic exit points. (B) Percentage of axons with moderate and severe branching in embryos injected with 3 ng of sema5A MO alone, 1 ng of plexin A3 MO alone and a combination of 3 ng sema5A MO and 1 ng plexin A3 MO. (C) Percentage of hemisegments observed with ectopic axonal exit points in embryos injected with 3 ng sema5A MO, 1 ng plexin A3 MO and a combination of 3 ng sema5A MO and 1 ng plexin A3 MO. Data quantified from 3 ng sema5A MO injections (n = 860 axons, 43 embryos), 1 ng plexin A3 MO injection (n = 2860 axons, 140 embryos) and 3 ng sema5A MO + 1ng plexin A3 MO injections (n = 2760 axons, 128 embryos). Ectopic axonal exit points were not observed in both wild-type uninjected or control MO-injected embryos (not shown). Error bars represent confidence interval for proportions at 95% confidence. Asterisks indicate significant difference between sema5A MO + plexinA3 MO injected and both 3 ng sema5A MO injected and plexinA3 MO injected at p < 0.01 using a Z-test of proportions. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
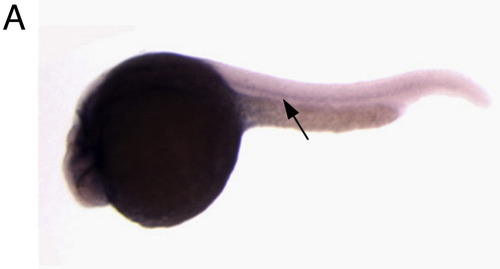
Sema5B is expressed in the notochord. In situ hybridization with antisense sema5b riboprobe at 24 hpf, lateral view, arrow indicates notochord expression. |

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 326(1), Hilario, J., Rodino-Klapac, L.R., Wang, C., and Beattie, C.E., Semaphorin 5A is a bifunctional axon guidance cue for axial motoneurons in vivo, 190-200, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.