- Title
-
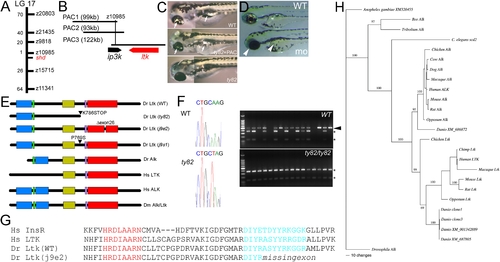
Leukocyte tyrosine kinase functions in pigment cell development
- Authors
- Lopes, S.S., Yang, X., Müller, J., Carney, T.J., McAdow, A.R., Rauch, G.J., Jacoby, A.S., Hurst, L.D., Delfino-Machín, M., Haffter, P., Geisler, R., Johnson, S.L., Ward, A., and Kelsh, R.N.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
shady mutants form an allelic series with reduced iridophores. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
shady mapping and identification as LTK orthologue. |
|
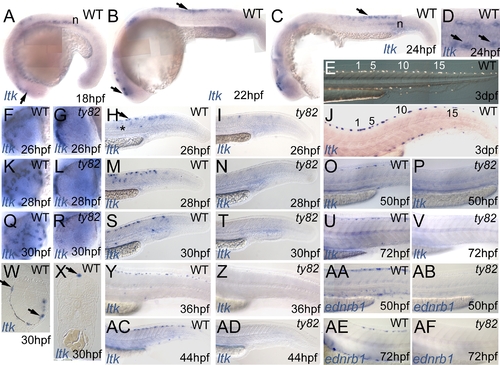
Expression pattern of zebrafish ltk in WT (A–D,F,H,J,K,M,O,Q,S,U,W–Y,AC) and shdty82 homozygous embryos (G,I,L,N,P,R,T,V,Z,AD) throughout embryonic development. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
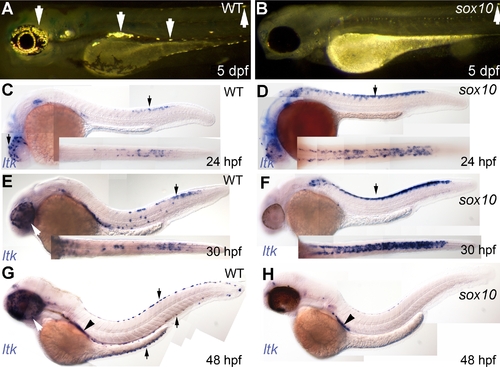
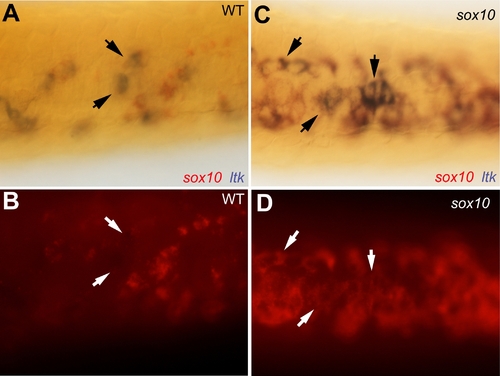
Iridophore phenotype and ltk expression patterns in sox10 mutants. |
|
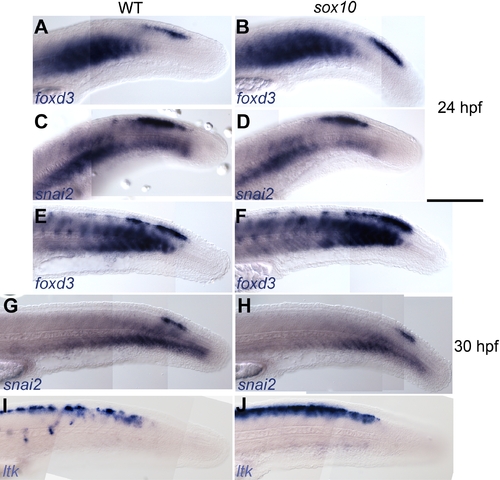
Early NC markers are unaffected in sox10 mutants. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Co-expression of sox10 in ltk-expressing cells in sox10 mutants. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
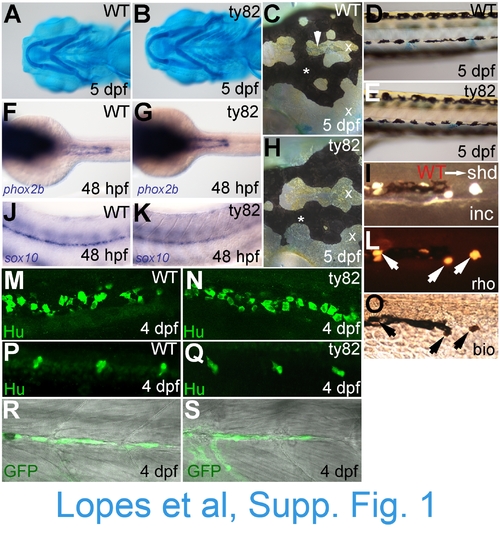
NC derivatives other than iridophores are overtly normal in shd(ty82) mutants. WT siblings (A,C,D,F,J,M,P,R) and shdty82 mutants (B,E,G,H,K,N,Q,S) are shown. A,B) Alcian blue staining of cartilage. C,H) Melanophores (*) and xanthophores (x) in head; iridophores in dorsal head indicated by arrowhead. D,E) Melanophores and xanthophores of posterior trunk. F,G) Enteric nervous system precursors (stained for phox2b mRNA). J,K) Glia of posterior lateral line nerve (sox10). M,N) Enteric neurons of posterior gut (anti-Hu). P,Q) Sensory neurons of tail dorsal root ganglia (anti-Hu immunostaining). R,S) Schwann cells of posterior lateral line nerve (eGFP from 4.9sox10:egfp transgene). Similarly, visual inspection of fin mesenchyme at 4 dpf, anti-Hu immunofluorescence labelling of sympathetic neurons and foxd3-labelled posterior lateral line glia showed no defects in shd mutants (data not shown). I,L,O)Transplants of WT cells into shdty82 mutants rescued iridophore formation (see Table 1). Part of ventral stripe of a 5 dpf WTàshdty82 chimaera to show rescued iridophores (I, incident light). Note that rescued iridophorot shown). I,L,O)Transplants of WT cells into shdty82 mutants rescued iridophore formation (see Table 1). Part of ventral stripe of a 5 des all show both lineage tracers (L, rhodamine dextran; O, biotinylated dextran). Stages as indicated. Embryos are shown in lateral view, except in A and B (ventral view) and C, F-H (dorsal view). |