Figure 12
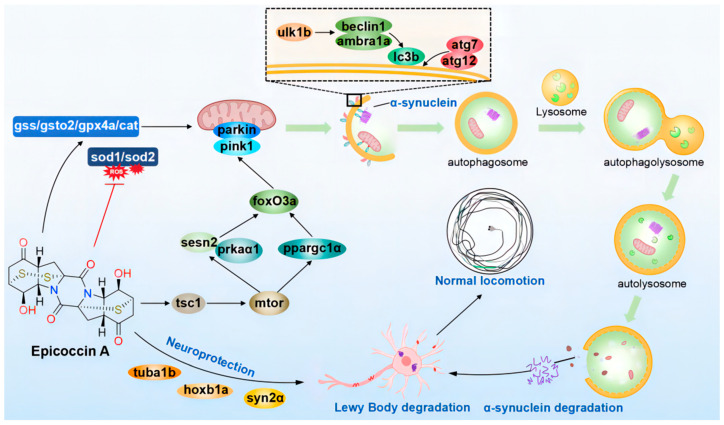
The proposed mechanism underlying the anti-PD effect of epicoccin A. Epicoccin A co-treatments can reverse the abnormal expressions of genes related to neuronal development, contributing to the improvement of neuronal damage in PD. Co-treatments with epicoccin A improved the aberrant gene expressions in the mTOR/FoxO signaling pathway, which might activate pink1/parkin-dependent mitophagy. This process facilitated the degradation of damaged mitochondria and α-synuclein fibrils, thereby inhibiting the formation of LBs. Moreover, epicoccin A co-treatments can inhibit oxidative stress by reducing ROS accumulation, further enhancing mitophagy and consequently alleviating the onset and development of PD.