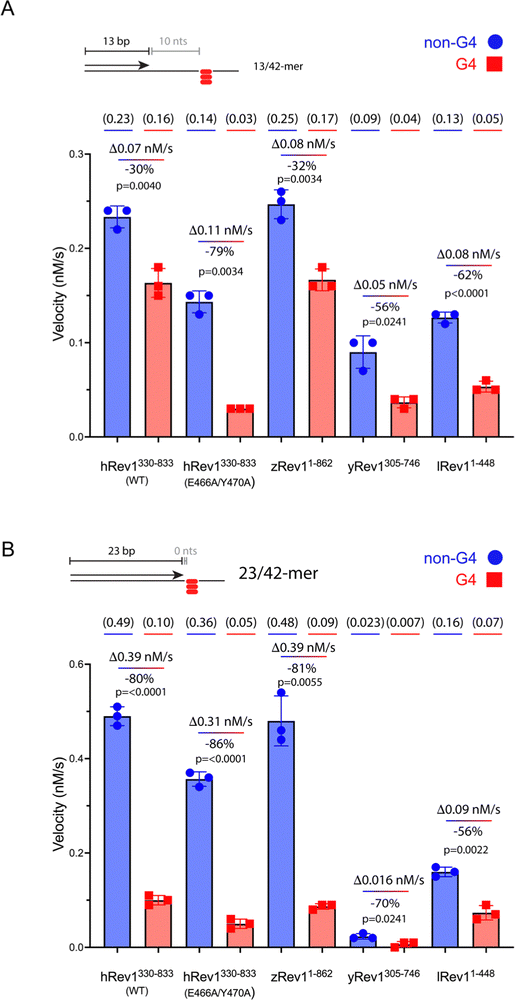
Fig. 2 Rev1 catalysis is sensitive to G4 positioning relative to the primer terminus. (A) Single-nucleotide insertion experiments were performed with hRev1 (WT and EY mutant), zRev1, yRev1, and lRev1. A 13-mer primer was annealed to a 42-mer template strand containing either a non-G4 control sequence or the Myc 14/23 G4 motif. The initial rate of dCMP insertion was measured (nM s−1) and plotted for each enzyme. The absolute value for the rate of product formation is shown in parentheses above each data column. The absolute difference between the non-G4 and G4 DNA substrates, along with normalized change in activity for the G4 substrate, is noted for each enzyme. (B) Single-nucleotide insertion experiments were performed with hRev1 (WT and EY mutant), zRev1, yRev1, and lRev1. A 23-mer primer was annealed to a 42-mer template strand containing either a non-G4 control sequence or the Myc 14/23 G4 motif. The initial rate of dCMP insertion was measured (nM s−1) and plotted for each enzyme. The absolute value for the rate of product formation is shown in parentheses above each data column. The absolute difference between the non-G4 and G4 DNA substrates, along with normalized change in activity for the G4 substrate, is noted for each enzyme. Results shown represent the mean (± std. dev.) for three independent replicates. In both panels, results are shown for non-G4 control DNA substrates (blue circles) and G4 DNA substrates (red squares). The percent decrease in activity was calculated for each enzyme by considering the non-G4 control to be 100% active compared to the G4 substrate. The reported p-values were calculated by using an unpaired Student's t-test with Welch's correction.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ RSC Chem Biol