Fig. 7 Lphn3.1 signals cell autonomously for pruning missorted DN axons
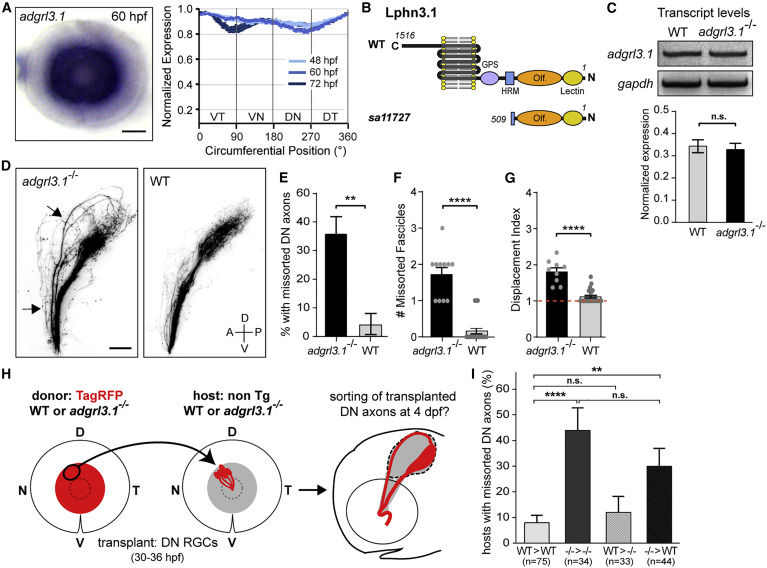
(A) adgrl3.1 ISH staining is detected throughout the RGC layer in the retina throughout development. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(B) Schematic of Lphn3.1 protein structure in WT and adgrl3.1sa11727 mutants. Olf, olfactomedin domain; HRM, hormone receptor motif; GPS, GPCR proteolysis site.
(C) Analysis of adgrl3.1 transcript levels by RT-PCR in WT and adgrl3.1 mutants at 4 dpf. Unpaired two-tailed t test, p = 0.71. Bars: standard errors.
(D) DN axons missort along the dorsal branch of the optic tract in adgrl3.1 mutants (arrows) but not in WT siblings at 4 dpf. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(E) Percentage of larvae with missorted DN axons at 4 dpf. One-sided chi-squared test with Yates’s correction, X2 (1, N = 50) = 6.125, p = 0.0067.
(F) Number of missorted DN axon fascicles in mutant larvae with sorting defects. Unpaired one-tailed t test, p ˂ 0.0001.
(G) Quantification of the displacement index in mutant larvae with sorting defects. Unpaired one-tailed t test, p ˂ 0.0001. n = 9 mutants.
(H) DN RGCs of an isl2b:TagRFP donor embryo (WT or adgrl3.1 mutant) were topographically transplanted between 30 and 36 hpf into the DN retina of a WT or adgrl3.1 mutant host. Pre-target sorting of transplanted donor DN axons was assessed at 4 dpf.
(I) Quantifications of the percentage of transplanted hosts with missorted donor DN axons. Chi-squared test, X2 (3, N = 186) = 22.51, p ˂ 0.0001. ∗∗p = 0.0023; ∗∗∗∗p ˂ 0.0001. Error bars: standard errors.
See also Figure S7.