Fig. 3
Fig. 3
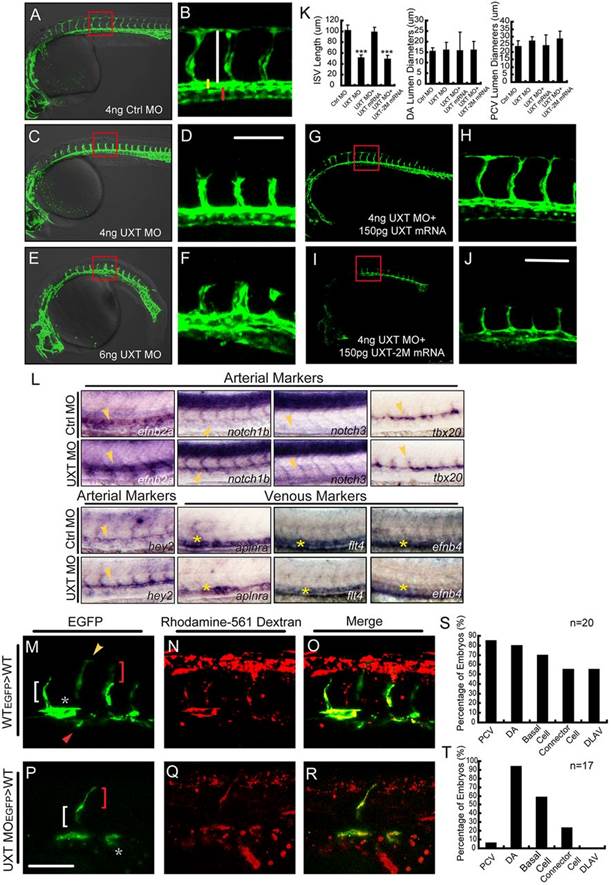
UXT is indispensable for zebrafish ISV spouting. (A-F) Confocal imaging of the UXT-deficient Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 embryos at 30hpf. (A,C,E) Bright-field images merged with confocal images. (B,D,F) Higher magnification images of the confocal-imaged area in the red boxed regions in A,C and E. (A) General morphology and trunk vascular phenotype and (B) the ISV sprouts in a Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 embryo injected with 4ng of control morpholino (Ctrl MO). (C) General morphology and trunk vascular phenotype, and (D) the ISV sprouts in a Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 embryo injected with 4ng of UXT morpholino (UXT MO). (E) General morphology and trunk vascular phenotype, and (F) the ISV sprouts in a Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 embryo injected with 6ng of UXT MO. The ISVs are marked by the vertical white line. The yellow and red bars indicate the lumen of the dorsal aorta (DA) and posterior cardinal vein (PCV), respectively. All of the embryos were confocal imaged at 30hpf and are shown in lateral views with rostral left and dorsal up. Scale bar:100µm. (G-J) Confocal imaging of the Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 morphants rescued by UXT mRNA. (H,J) The confocal imaged area of the red boxed regions in G and I. (G) The trunk vascular phenotype and (H) the ISV sprouts in a Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 embryo injected with 4ng of UXT morpholino plus 150pg of wild-type UXT mRNA (4ng UXT MO+150pg UXT mRNA). (I) The trunk vascular phenotype and (J) the ISV sprouts in a Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 embryo injected with 4ng of UXT MO plus mutant UXT mRNA (4ng UXT MO+150pg UXT-2M mRNA). All of the embryos were confocal imaged at 30hpf. Scale bar: 100µm. (K) Statistical analysis of the ISV length and the lumen diameter of the DA or PCV from embryos injected with Ctrl MO, UXT MO, UXT MO+UXT mRNA or UXT MO+UXT-2M mRNA. For one experiment, six embryos of each treatment were analyzed at 30hpf. Data show the mean±s.e.m. (at least three independent experiments); ***P<0.001 versus the corresponding control. (L) The whole-mount in situ hybridization of UXT-deficient embryos at 30hpf. Riboprobes are against the arterial markers efn2a, notch1, notch3, tbx20, hey2 and the venous markers aplnra, flt4 and efnb4. The yellow arrowheads denote the DA; the yellow asterisks indicate the PCV. (M-R) Confocal imaging of the donor Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 cells in non-transgenic embryos at 30hpf. (M) Wild-type cells contribute to all trunk vessels, including the DA (asterisk), PCV (red arrowhead), basal cells (red bracket), connector cells (white bracket) and DLAV (yellow arrowhead). (P) Deficient for UXT, the endothelial cells of Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 can only contribute to theDA, basal cells and connector cells. (N,Q) The transplanted donor cells were stained with Rhodamine-561 dextran. (O,R) Merged images of EGFP and Rhodamine-561 dextran. Scale bar: 75µm. (S,T) Quantification of wild-type (S) and UXT-deficient (T) donor Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 cells in non-transgenic embryos. n, the number of successfully transplanted embryos.