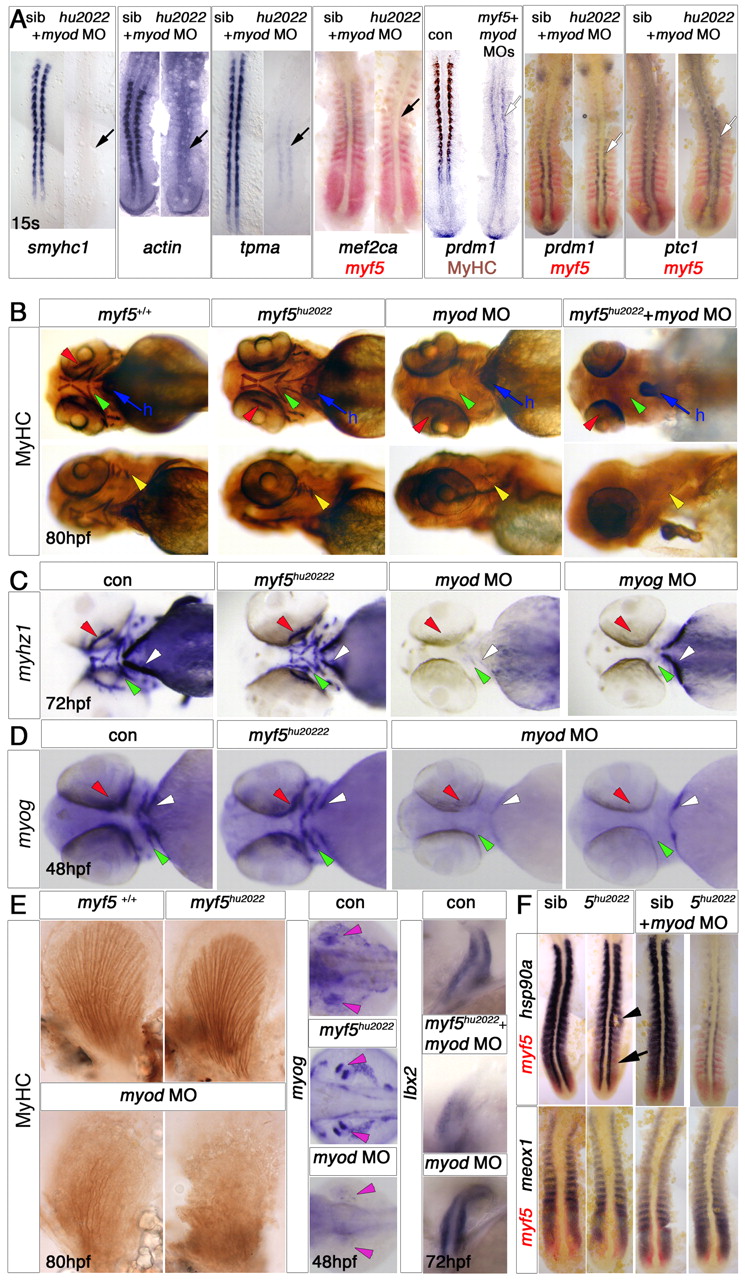
Fig. 3 Myf5 requirement differs between somitic, head and fin muscle development. In situ mRNA hybridisation and/or MyHC immunohistochemistry of control and morphant wild-type or myf5+/hu2022 incross embryos. Dorsal flatmounts with anterior to top (A,F), or whole-mounts with anterior to left in ventral (B, upper row, C,D), lateral (B, lower row) or dorsal (E) view. (A) myf5hu2022 mutants injected with myod MO show a loss of the adaxial slow muscle differentiation markers smyhc1, actin, tpma and mef2ca and MyHC immunostaining (black arrows), but retain other adaxial markers such as prdm1 and ptc1 (white arrows). (B-D) Head muscles are present in 80 hpf myf5hu2022 mutants but are missing from embryos injected with myod (B,C) or myog MO (C). Arrowheads indicate lack of ventral (green), dorsal (yellow), extra-ocular (red) and sternohyoideus (sh, white) muscles. All embryos show normal heart (h, blue arrow). Note the presence of sternohyoideus in myog morphants. All embryos from a myf5+/hu2022 incross have normal expression of myhz1 at 72 hpf (C) and myog at 48 hpf (D) in the head. myod morphants lack myog mRNA (19/21), although sternohyoideus was still detected in some embryos (6/21). (E) In pectoral fin, myog mRNA in muscle masses (pink arrowheads) and MyHC are ablated or reduced by loss of Myod, but not by loss of Myf5. Ibx2 mRNA is unaffected by myod MO. (F) Expression of hsp90a is delayed in fast muscle precursors (arrow) of the myf5hu2022 mutant and recovers in somites (arrowhead), but is drastically reduced throughout the axis in myf5hu2022 mutants injected with myod MO, both in slow and fast precursors. meox1 expression is unchanged in fast precursors.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development