Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250909-41
- Publication
- Varga et al., 2025 - Transposon insertion causes ctnnb2 transcript instability that results in the maternal effect zebrafish ichabod (ich) mutation
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
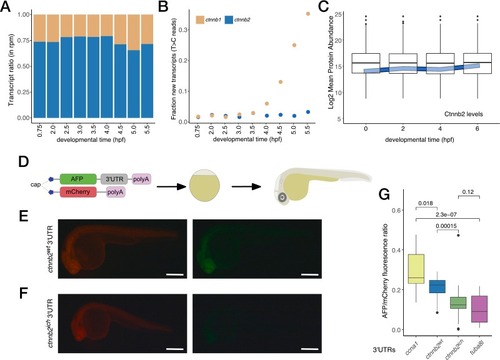
High stability of maternal ctnnb2 transcripts is disrupted by 3’UTR transposon insertion. (A) Transcriptome analysis of maternal ctnnb1 and ctnnb2 mRNAs shows a heightened abundance of maternal ctnnb2 transcripts throughout early development (rpm – reads per million bp, ctnnb1 transcripts are shown in beige, ctnnb2 transcripts in blue). (B) Metabolic labelling suggests active transcription of ctnnb1 after ZGA, but no expression of ctnnb2. (Data for panels A and B are derived from [41]. (C) Maternal Ctnnb2 protein levels are also very stable during early stages of development as compared to mean protein abundances at these timepoints. (Data from [43]. (D) Experimental scheme used to test the effect of 3’UTRs on the stability of mRNAs. In vitro transcribed AFP mRNAs with different 3’UTRs are combined with mCherry transcripts with invariant 3’UTRs and injected into 1-cell stage zebrafish embryos. Fluorescence intensity for both AFP and mCherry is measured at 24 hpf. (E, F) Typical fluorescence observed in embryos injected with AFP carrying ctnnb2wt or ctnnb2ich 3’UTRs, respectively. (Scale bars: 0.5 mm) (G) Relative fluorescence intensities observed in embryos injected with different 3’UTRs compared to stable and unstable controls (ccna1 and tuba8l 3’UTRs, respectively). (Pairwise p values were calculated with the Kruskal-Wallis test.) |
Reprinted from Biochimica et biophysica acta. Gene regulatory mechanisms, , Varga, Z., Kagan, F., Maegawa, S., Nagy, Á., Okendo, J., Burgess, S.M., Weinberg, E.S., Varga, M., Transposon insertion causes ctnnb2 transcript instability that results in the maternal effect zebrafish ichabod (ich) mutation, 195104195104, Copyright (2025) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ BBA Gene Regulatory Mechanisms