Fig. 4
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-250218-79
- Publication
- Wang et al., 2025 - Direct lysine dimethylation of IRF3 by the methyltransferase SMYD3 attenuates antiviral innate immunity
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
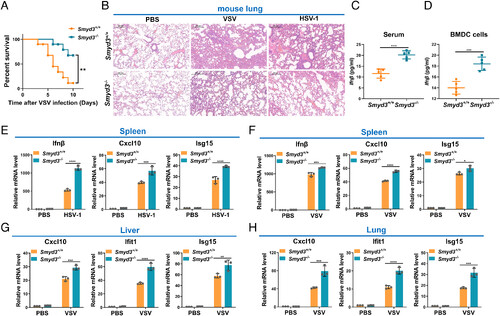
Disruption of Smyd3 in mice results in increased susceptibility to lethal viral infection. (A) Survival (Kaplan–Meier curve) of Smyd3+/+ (n = 10) and Smyd3−/− (n = 10) mice by intraperitoneal injection of VSV (1 × 107 plaque-forming units (PFU)/ per mouse) and monitored for 10 d. **P < 0.01. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained images of lung sections from Smyd3+/+ or Smyd3−/− mice injected intraperitoneally with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (vehicle control), VSV (1 × 107 PFU/per mouse) or HSV-1 (5 × 107 PFU/per mouse) for 24 h. (C) ELISA of Ifnβ in the serum of Smyd3+/+ or Smyd3−/− mice injected intraperitoneally with VSV (1 × 107 PFU/per mouse) for 24 h. (D) ELISA of Ifn-β in the supernatant of Smyd3+/+ or Smyd3−/− BMDCs infected with VSV for 8 h. (E) qPCR analysis of Ifnβ, Cxcl10, and Isg15 mRNA in spleens of Smyd3+/+ or Smyd3−/− mice injected intraperitoneally with PBS or HSV-1 (5 × 107 PFU/per mouse) for 24 h. (F) qPCR analysis of Ifnβ, Cxcl10, and Isg15 mRNA in spleens of Smyd3+/+ or Smyd3−/− mice injected intraperitoneally with PBS or VSV (1 × 107 PFU/per mouse) for 24 h. (G) qPCR analysis of Cxc10, Ifit1, and Isg15 mRNA in the liver of Smyd3+/+ or Smyd3−/− mice injected intraperitoneally with PBS or VSV (1 × 107 PFU/per mouse) for 24 h. (H) qPCR analysis of Cxcl10, Ifit1, and Isg15 mRNA in the lungs of Smyd3+/+ or Smyd3−/− mice injected intraperitoneally with PBS or VSV (1 × 107 PFU/per mouse) for 24 h. PBS, phosphate buffer saline; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. Data are presented as the mean values of a representative experiment performed in triplicate (E–H) or as representative data (B); these experiments were repeated independently at least three times, and error bars indicate S.D. |